Learning Objectives
advertisement

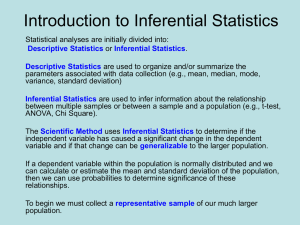
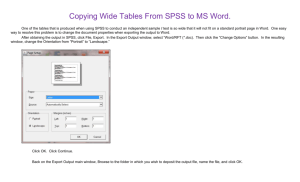
EDF 802 Dr. Jeffrey Oescher Topic 1 Learning Objectives Revised 23 January 2014 1. Review of descriptive statistics 1.1. Means 1.1.1.Define the term mean. 1.1.2.Identify the difference between a norm referenced and criterion referenced interpretation of a mean score. 1.1.3.Calculate a mean score and interpret it from a norm referenced perspective. 1.1.4.Calculate a mean score and interpret it from a criterion referenced perspective. 1.2. Variance and standard deviation 1.2.1.Define the term variance. 1.2.2.Define the term standard deviation. 1.2.3.Describe the characteristics of the standard deviation relative to the normal curve. 1.2.4.Calculate a standard deviation and interpret it in terms of the magnitude of variation of the scores (i.e., small, moderate, large). 1.3. Correlation coefficient 1.3.1.Define the term correlation coefficient. 1.3.2.Explain the meaning of the magnitude of a correlation coefficient. 1.3.3.Explain the meaning of the direction of a correlation coefficient. 1.3.4.Calculate a correlation coefficient and interpret it in terms of both magnitude and direction. 2. Review of SPSS 2.1. Creating SPSS files 2.1.1.Create a SPSS data file. 2.1.2.Create a SPSS syntax file. 2.1.3.Generate a SPSS output file. 2.2. Managing and manipulating data 2.2.1.Manage a SPSS data file using the DATA pull down menu commands. 2.2.2.Create a variable using the TRANSFORM pull down menu commands. 2.2.3.Generate frequencies, means, standard deviations, and correlations using the ANALYZE pull down menu commands. 3. Statistical inferences 3.1. Parameters and statistics 3.1.1.Differentiate a population parameter from a sample statistic. 3.1.2.Identify the Greek letters that represent specific population parameters. 3.1.3.Identify the Arabic symbols that represent specific sample statistics. 3.1.4.Create a Word text file containing the common Greek letters and Arabic symbols relevant to statistical analyses. 1 3.2. Sampling distributions 3.2.1.Define the term sampling distribution. 3.2.2.Explain how a sampling distribution of the mean can be created. 3.2.3.Identify the “mean” and standard deviation” of a sampling distribution of the difference between two means. 3.2.4.Identify three common sampling distributions. 3.2.5.Explain what is meant by “a family of t-distributions.” 4. Hypothesis testing 4.1. Statistical hypotheses 4.1.1.Describe the general characteristics of a null hypothesis and create the symbol for a null hypothesis in Word. 4.1.2.Describe the general characteristics of an alternative hypothesis and create the symbol for an alternative hypothesis in Word. 4.2. Inferential test statistics 4.2.1.Explain the reason for considering a z-score a “standard” score. 4.2.2.Explain the general form of an inferential test statistic and compare this to the formula for a z-score. 4.2.3.Explain the formula for an inferential test of the differences between two means and compare this formula to that of a z-score. 4.3. Hypothesis tests 4.3.1.Identify the six steps required to test a statistical hypothesis. 4.3.2.Explain the role of the alpha level in the test of a statistical hypothesis. 4.3.3.Analyze data inferentially using SPSS procedures, interpret the output, and explain in detail each of the six steps for testing hypotheses relative to this analysis. 2