Study Guide
advertisement

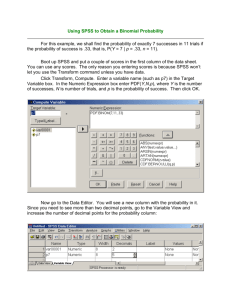
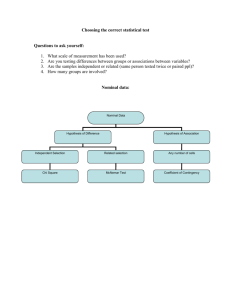
Study Guide for Quantitative Analysis HPELS 6210 Spring 2015 Chapter 1. Introduction to Statistics 1. Relative to the topic of statistics, be able to define the following terms: population, sample, variable, data, parameter, statistic, sampling error, independent variable, dependent variable, discrete variable, continuous variable 2. Be able to distinguish between descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. 3. Be able to categorize variables within a study as being independent or dependent. 4. be able to define and distinguish between the following scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio Chapter 2. Frequency Distributions 1. Be able to define frequency distribution and be able to produce histograms and polygons of frequency distribution using SPSS. 2. Be able to define and draw a symmetrical distribution and a skewed distribution. 3. Be able to define positively skewed and negatively skewed. 4. Be able to define percentile rank, percentile, cumulative frequency, cumulative percentage 5. Using SPSS be able to produce frequency distribution tables, frequency distribution histograms and frequency distribution bar graphs. Chapter 3. Central Tendency 1. Be able to define central tendency, mean, median, and mode. 2. Given the shape of a distribution, be able to estimate the mean, median, and mode. 3. Unsing SPSS, be able to compute the mean of a distribution of scores. Chapter 4. Variability 1. Be able to define variability, range, standard deviation and variance. 2. Understand the difference between the standard deviation of a population and the standard deviation of a sample. 3. Be able to define degrees of freedom and know how to calculate the degrees of freedom in a sample. 4. Using SPSS, be able to calculate the range, standard deviation and variance of a sample. Chapter 5. z-Scores 1. Understand the definition of z scores and the relationship of z scores to a distribution. 2. Be able to determine a raw score from a z score. 3. Be able to standardize a distribution using z scores and know when using a standardized distribution is appropriate. 4. Be able to compare raw scores from different distributions. 5. Be able to use SPSS to transform raw scores into z scores. Chapter 6. Probability 1. Be able to define random sample and independent random sample. 2. Be able to draw and identify the characteristics of a normal distribution. 3. Be able to use the unit normal table and be able to locate z scores and proportions in a normal distribution. Chapter 7. Probability and Samples 1. Be able to define sampling error, distribution of sample means, sampling distribution, Central limit theorem, standard error of M. 2. Know the relationship of sample size, the sample mean, the population mean, and the standard errorl 3. Know the difference between a population of scores, a sample selected from the population and the distribution of sample means. Chapter 8. Intro to Hypothesis Testing 1. Understand the purpose of a hypothesis test. 2. Be able to define null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis (directional hypothesis), alpha level, (level of significance), critical region, type I error, type II error, effect size, and statistical power. 3. Know the four steps used in hypothesis testing. 4. Know the three assumptions that must be made in order to perform hypothesis tests with z-scores 5. Be able to distinguish between one-tailed and two-tailed tests of significance. 6. Know how to calculate effect size (Cohen’s d) and how to evaluate effect size. 7. Understand the effect of sample size, size of the treatment effect, and the alpha level on statistical power. Chapter 9. Intro to the t Statistic 1. Be able to define the estimated standard error and the t distribution. 2. Understand why hypothesis testing using a t-test is used rather than using a z-score. 3. Be able to determine probabilities and proportions using a table for the t distribution. 4. Understand the use of the estimated Cohen’s d and the percentage of variance explained, and a confidence interval to measure effect size. 5. Be able to interpret the results of hypothesis testing using the t statistic. 6. Be able to use SPSS to test a hypothesis using a One-Sample t test. Chapter 10. The t Test for Two Independent Samples 1. Understand when a t test for independent samples should be used to test a hypothesis. Be able to explain a between subject’s design. 2. Know the three assumptions underlying the independent-measures t test. 3. Using SPSS , be able to perform and interpret a hypothesis test for two independent samples. Chapter 11. The t Test for two Related Samples 1. Be able to explain a repeated-measures design or within-subjects design and know when such a design is appropriate. 2. Be able to explain a matched-subjects design. 3. Using SPSS, be able to perform and interpret a hypothesis test for two related samples. Chapter 12. Intro to ANOVA 1. Know when it is appropriate to use ANOVA as opposed to a t test. 2. Be able to define factors and levels as they pertain to ANOVA. 3. Know the difference between the way the t statistic and the F ratio is computed. 4. Understand the reason an F ratio is used with more than two groups (the effect on the Type 1 error when doing multiple t tests) 5. Know how to determine the within-treatment degrees of freedom and the between-treatment degrees of freedom. 6. Understand the purpose of post hoc tests and know the names of the two most commonly used post hoc tests (Tukey’s and Scheffe) 7. Using SPSS, be able to perform and interpret a hypothesis test for two or more groups. Chapter 13. Repeated Measures ANOVA 1. Using SPSS, be able to perform and interpret a hypothesis test for a repeated measures ANOVA. Chapter 15. Correlation 1. Be able to define correlation and know the meaning of positive and negative correlations and be able to interpret the absolute value of the correlation coefficient. 2. Know when to use the Pearson correlation. 3. Understand the use of correlations for the purpose of prediction, validity, reliability and theory verification. 5. Be able to determine whether or not a correlation is significant for a given alpha level. 6. Using SPSS, be able to perform and interpret a correlational analysis.