Answers
advertisement

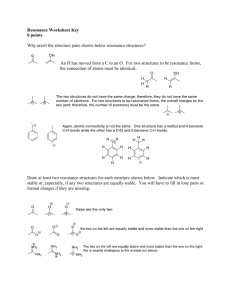
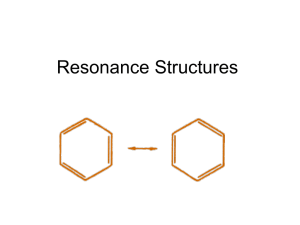
Drawing Resonance Structures Major concepts Looking at a Lewis structure, you can see features that let you know that there are additional resonance structures. There are patterns that you can use to draw acceptable resonance structures in a systematic way. Although a resonance structure may be acceptable, that doesn’t mean we will always draw it. It may be acceptable but insignificant. Vocabulary Acceptable resonance structure Significant resonance structure Resonance stabilization Students should be able to: Recognize molecules that display resonance based on their structure Draw all significant resonance structures given a starting structure Answer some questions that apply resonance concepts Daily Problems 1. Organic as a Second Language chapter 2 problems 2.1-2.73 Cumulative Problems These are extremely important cumulative problems because they are starting to get similar to what you will see throughout the rest of the course. In these problems, and from now on, you should always draw resonance structures and consider their impact on stability before answering the problem. 2. Which carbon atom in 1-aminoprop-1-ene is most electron rich? Explain. The second carbon is more electron rich due to the resonance structure shown above. 3. This compound could, in principle, undergo a reaction in which it lost an H+ to form one or the other of these anions. Which product will form preferentially? (Remember—first consider resonance, then consider its effect on stability.) Due to the resonance-stabilized product that will form, the boxed compound will be preferentially formed. 4. Proteins are formed when amino acids are stuck together through “peptide bonds”, which chemists call amides. Proteins have a particular structure and they function the way they do because the carbonnitrogen bond of an amide acts sort of like a single bond and sort of like a double bond. Look at the structure below, which is part of a protein. How can this bond act sort of like a double bond when the Lewis structure looks like a single bond? Amides have a resonance structure that places the negative charge on the oxygen, causing the bond between the nitrogen and carbon to act like both a single and a double bond. 5. Name all the functional groups in the molecule in problem 4. Keep in mind that if the functional group has lost H+ (and is therefore now negative), we say it is a “deprotonated” functional group. If the functional group has gained an H+ and is now positive, we say that it is a “protonated” functional group. thiol amide Deprotonated carboxylic acid Protonated amine Extension problems 6. Redraw these incorrectly drawn Lewis structures. How are they incorrectly drawn? What do you think the physical reason is that the molecules are not in the shapes drawn below? Atoms want to be as far away as they possibly can within a compound to avoid “knocking into” other atoms (i.e. steric clashing).