WS 2 Research Project Topics
advertisement
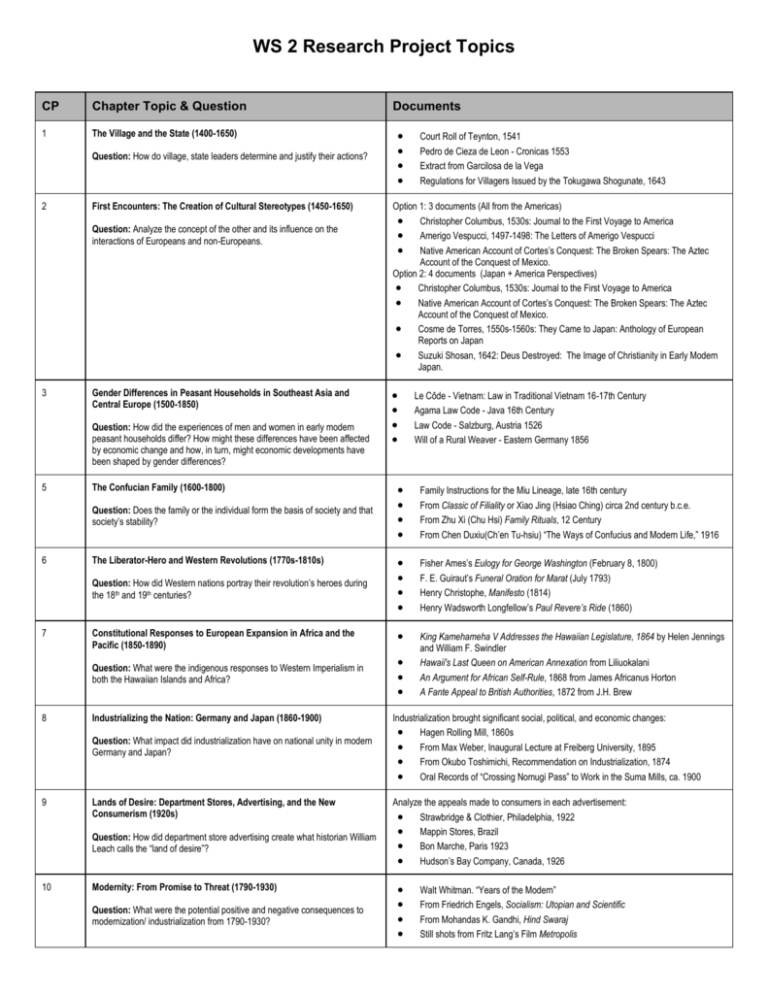
WS 2 Research Project Topics CP Chapter Topic & Question 1 The Village and the State (1400-1650) Question: How do village, state leaders determine and justify their actions? 2 First Encounters: The Creation of Cultural Stereotypes (1450-1650) Question: Analyze the concept of the other and its influence on the interactions of Europeans and non-Europeans. 3 Gender Differences in Peasant Households in Southeast Asia and Central Europe (1500-1850) Question: How did the experiences of men and women in early modern peasant households differ? How might these differences have been affected by economic change and how, in turn, might economic developments have been shaped by gender differences? 5 The Confucian Family (1600-1800) 7 8 Option 1: 3 documents (All from the Americas) Christopher Columbus, 1530s: Journal to the First Voyage to America Amerigo Vespucci, 1497-1498: The Letters of Amerigo Vespucci Native American Account of Cortes’s Conquest: The Broken Spears: The Aztec Account of the Conquest of Mexico. Option 2: 4 documents (Japan + America Perspectives) Christopher Columbus, 1530s: Journal to the First Voyage to America Native American Account of Cortes’s Conquest: The Broken Spears: The Aztec Account of the Conquest of Mexico. Cosme de Torres, 1550s-1560s: They Came to Japan: Anthology of European Reports on Japan Suzuki Shosan, 1642: Deus Destroyed: The Image of Christianity in Early Modern Japan. Le Côde - Vietnam: Law in Traditional Vietnam 16-17th Century Agama Law Code - Java 16th Century Law Code - Salzburg, Austria 1526 Will of a Rural Weaver - Eastern Germany 1856 Question: How did Western nations portray their revolution’s heroes during the 18th and 19th centuries? Fisher Ames’s Eulogy for George Washington (February 8, 1800) F. E. Guiraut’s Funeral Oration for Marat (July 1793) Henry Christophe, Manifesto (1814) Henry Wadsworth Longfellow’s Paul Revere’s Ride (1860) Constitutional Responses to European Expansion in Africa and the Pacific (1850-1890) Question: What were the indigenous responses to Western Imperialism in both the Hawaiian Islands and Africa? King Kamehameha V Addresses the Hawaiian Legislature, 1864 by Helen Jennings and William F. Swindler Hawaii's Last Queen on American Annexation from Liliuokalani An Argument for African Self-Rule, 1868 from James Africanus Horton A Fante Appeal to British Authorities, 1872 from J.H. Brew The Liberator-Hero and Western Revolutions (1770s-1810s) Industrializing the Nation: Germany and Japan (1860-1900) Lands of Desire: Department Stores, Advertising, and the New Consumerism (1920s) Question: How did department store advertising create what historian William Leach calls the “land of desire”? 10 Court Roll of Teynton, 1541 Pedro de Cieza de Leon - Cronicas 1553 Extract from Garcilosa de la Vega Regulations for Villagers Issued by the Tokugawa Shogunate, 1643 Family Instructions for the Miu Lineage, late 16th century From Classic of Filiality or Xiao Jing (Hsiao Ching) circa 2nd century b.c.e. From Zhu Xi (Chu Hsi) Family Rituals, 12 Century From Chen Duxiu(Ch’en Tu-hsiu) “The Ways of Confucius and Modern Life,” 1916 Question: What impact did industrialization have on national unity in modern Germany and Japan? 9 Question: Does the family or the individual form the basis of society and that society’s stability? 6 Documents Modernity: From Promise to Threat (1790-1930) Question: What were the potential positive and negative consequences to modernization/ industrialization from 1790-1930? Industrialization brought significant social, political, and economic changes: Hagen Rolling Mill, 1860s From Max Weber, Inaugural Lecture at Freiberg University, 1895 From Okubo Toshimichi, Recommendation on Industrialization, 1874 Oral Records of “Crossing Nomugi Pass” to Work in the Suma Mills, ca. 1900 Analyze the appeals made to consumers in each advertisement: Strawbridge & Clothier, Philadelphia, 1922 Mappin Stores, Brazil Bon Marche, Paris 1923 Hudson’s Bay Company, Canada, 1926 Walt Whitman. “Years of the Modern” From Friedrich Engels, Socialism: Utopian and Scientific From Mohandas K. Gandhi, Hind Swaraj Still shots from Fritz Lang’s Film Metropolis 11 The Industrial Crisis and the Centralization of Government (1924-1939) Question: Compare how major industrialized nations chose to combat the Great Depression. 12 Total War: The Cost of Unlimited Conflict (1914-1945) Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig, “Features of the War” Paul Valery, “The Crisis of the Spirit” Erich Maria Remarque, All Quiet on the Western Front Kande Kamara, “Memories of a West African in France” (from John Reilly, Worlds of History: A Comparative Reader) Part Two: How did total war influence both government policy and civilian populations? Reischsmarschal Hermann Goering, German Radio Broadcast Iwo Nakamura, Recollections of August 6, 1945 Henry L. Stimson, “The Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb” Jean-Francois Steiner, Treblinka (from John Reilly, Worlds of History: A Comparative Reader) Crucible of Conflict: The Suez Crisis (1956) Gamal Abdel Nasser Announces the Nationalization of the Suez Canal 8&9 (together) Exchange of letters between President Eisenhower and PM Eden A Statement by Jawarharlal Nehru, Indian Prime Minister Soviet Response to the Aggression Against Egypt Question: How strong were women’s arguments for peace from 1910-1990? Jane Addams on Women and War Huda Sha’rawi, Speech to the Congress of … Miyako Shinohara “In the Name of Peace” Coretta Scott King on Women and the Nuclear Arms Race, 1984 McDomination: The Americanization of Global Popular Culture (1950s to the Present) Advertisement from McDonald's restaurant Oslo, Norway A McDonald's Promotion in Hong Kong, 1998 from Washington Post October 11, 1998 The French Protest McDonald's from The Times (London) September 1, 1999 Big Mac II: How McDonald's Became Global by Thomas L. Friedman New York Times, December 11, 1996 Question: How did international rivalries and ideology impact regional conflict during the Cold War? 14 15 Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald, February 12, 1931: Parliamentary Debates: House of Commons President Franklin Roosevelt, April 14, 193- Nothing to Fear: The Selected Addresses of FDR Chancellor Adolf Hitler: The Speeches of Adolf Hitler, April 1922- August 1939 Hashimoto Kingoro, Address to Young Men: Sources of Japanese Tradition Supplemental Documents: Formatted in Charts Unemployment Charts: League of Nations, Monthly Bulletin of Statistics. Central government Revenues Expenditures in National Currencies: European Historical Statistics Sizes of Armies, Great Britain, US and Germany: The Oxford History of the British Army Armed Services Spending as a Percentage of Total Government Expenditures in Japan: Rise and Fall of the Great Powers: Economic Change and Military Conflict from 1500 to 2000 Part One: How did World War I change the way people felt about war? 13 Feminism and the Peace Movement (1910-1990) Question: How did the Americanization of popular culture impact other cultures that consume American products? Greeks/ Romans Greeks/Romans Enlightenment Thinkers Enlightenment Thinkers Between the Wars Between the Wars Question: How did early civilizations help develop modern Democratic ideas? Question: What were the Enlightenment’s philosophical views of humanity and human rights? Question: What philosophies grew out of the outcomes of the first World War? Plato’s The Republic Aristotle’s PoliticsThe Ten Commandments Rome’s 12 Tables John Locke - Treatise on Government Thomas Hobbes - The Leviathan Rousseau - The Social Contract Wollstonecraft - Vindication on the Rights of Women Lenin - April Theses Mussolini - On Fascism Wilson - 14 Points Hitler - Mein Kampf