Cells homework
advertisement

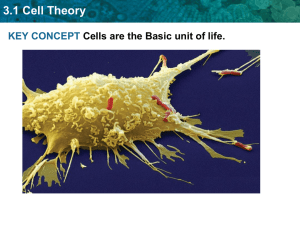
Cells Two Types of Cells There is another basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains, and protects, most of the cell's DNA. Based on whether they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the most common organisms today. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Eukaryotic cells also contain other organelles besides the nucleus. An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm that performs a specific job in the cell. Organelles called mitochondria, for example, provide energy to the cell, and organelles called vacuoles store substances in the cell. Organelles allow eukaryotic cells to carry out more functions than prokaryotic cells can. This allows eukaryotic cells to have greater cell specificity than prokaryotic cells. Ribosomes, the organelle where proteins are made, are the only organelles in prokaryotic cells. In some ways, a cell resembles a plastic bag full of Jell-O. Its basic structure is a plasma membrane filled with cytoplasm. Like Jell-O containing mixed fruit, the cytoplasm of the cell also contains various structures, such as a nucleus and other organelles. Does a cell have its own ER? Yes, but in this case, the ER is not just for emergencies. True, there might be times when the cell responds to emergency conditions and the functions of the ER may be needed, but usually the cell's ER is involved in normal functions. Proteins are also made on the outside of the ER, and this starts a whole process of protein transport, both around the inside of the cell and to the cell membrane and out. Other Organelles In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells have many other organelles, including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, and centrioles. Endoplasmic Reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of phospholipid membranes that form hollow tubes, flattened sheets, and round sacs. The ER has two major functions: Transport: Molecules, such as proteins, can move from place to place inside the ER, much like on an intracellular highway. Synthesis: Ribosomes that are attached to ER, similar to unattached ribosomes, make proteins. Lipids are also produced in the ER. Golgi Apparatus The Golgi apparatus is a large organelle that is usually made up of five to eight cup-shaped, membranecovered discs called cisternae. The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages different substances for secretion out of the cell, or for use within the cell. The Golgi apparatus is found close to the nucleus of the cell, where it modifies proteins that have been delivered in transport vesicles from the RER. It is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell. Pieces of the Golgi membrane pinch off to form vesicles that transport molecules around the cell. The Golgi apparatus can be thought of as similar to a post office; it packages and labels "items" and then sends them to different parts of the cell. Both plant and animal cells have a Golgi apparatus. Vesicles A vesicle is a small, spherical compartment that is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. Vesicles are basic tools of the cell for organizing metabolism, transport, and storage of molecules. Vesicles are also used as chemical reaction chambers. They can be classified by their contents and function. Lysosomes are vesicles that are formed by the Golgi apparatus. They contain powerful enzymes that could break down (digest) the cell. Lysosomes break down harmful cell products, waste materials, and cellular debris and then force them out of the cell. They also digest invading organisms such as bacteria. Lysosomes also break down cells that are ready to die, a process called autolysis. Vacuoles Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that can have secretory, excretory, and storage functions. Many organisms will use vacuoles as storage areas and some plant cells have very large vacuoles. Centrioles Centrioles are rod-like structures made of short microtubules. Centrioles are very important in cellular division, where they arrange the mitotic spindles that pull the chromosome apart during mitosis. Instructions: Define bold faced words, answer questions, and write summary 1. What are the 2 types of cells? 2. List each organelle and its function. Cells Two Types of Cells There is another basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains, and protects, most of the cell's DNA. Based on whether they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the most common organisms today. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Eukaryotic cells also contain other organelles besides the nucleus. An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm that performs a specific job in the cell. Organelles called mitochondria, for example, provide energy to the cell, and organelles called vacuoles store substances in the cell. Organelles allow eukaryotic cells to carry out more functions than prokaryotic cells can. This allows eukaryotic cells to have greater cell specificity than prokaryotic cells. Ribosomes, the organelle where proteins are made, are the only organelles in prokaryotic cells. In some ways, a cell resembles a plastic bag full of Jell-O. Its basic structure is a plasma membrane filled with cytoplasm. Like Jell-O containing mixed fruit, the cytoplasm of the cell also contains various structures, such as a nucleus and other organelles. Does a cell have its own ER? Yes, but in this case, the ER is not just for emergencies. True, there might be times when the cell responds to emergency conditions and the functions of the ER may be needed, but usually the cell's ER is involved in normal functions. Proteins are also made on the outside of the ER, and this starts a whole process of protein transport, both around the inside of the cell and to the cell membrane and out. Other Organelles In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells have many other organelles, including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, and centrioles. Instructions: Define bold faced words, answer questions, and write a summary. 1. What are the two types of cells? 2. How is a cell like jello? 3. List 4 organelles of the cell.