Chapter 4 - 4.1 PowerPoint
advertisement

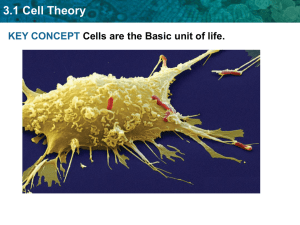
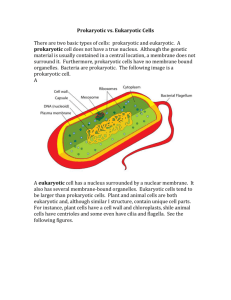
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. 3.1 Cell Theory In the 1600’s he was the first scientist to describe living cells using a simple microscope (contained one lens). Anton van Leeuwenhook 3.1 Cell Theory • He was an English scientist who lived at the same time as van Leeuwenhoock. •Hooke was the first to identify cells and name them. • He observed that cork was composed of tiny, hollow boxes that he called “CELLS”. Robert Hooke 3.1 Cell Theory German scientist who observed many types of plants and determined that all plants consist of cells. Matthias Schleiden 3.1 Cell Theory German scientist who determined that all animals consist of cells. Theodor Schwann 3.1 Cell Theory Rudolf Virchow • Proposed that all cells come from other cells. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. • More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. • More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. • The cell theory is a unifying concept of biology. 3.1 Cell Theory The History of the Cell Theory Before microscopes were invented, diseases were thought to be caused by curses and supernatural events. By using microscopes scientists realized they were entering a new world---one of microorganisms. Microscopes enabled scientists to view and study cells. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. 3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics. 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed by a membrane. cell membrane Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. cell membrane cytoplasm Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. nucleus cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. nucleus Eukaryotic cells have membranebound organelles. organelles (multi-cellular organisms) cell membrane ex. -humans -other animals 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. nucleus organelles cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. nucleus • Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles. • AKA (Unicellular organisms) ex. bacteria organelles virus cell membrane cytoplasm