regions meiosis

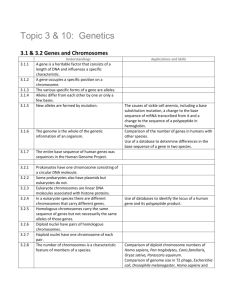
GENETICS
The Study of the transmission/inheritance of traits through generations
Inherited genetic variation is studied at the level of
Individuals and their offspring o Where genetic information resides(In the Genome)
Eukaryotic cells store DNA
In Bacteria: DNA of the nucleoid region
In virus: DNA or RNA included in the head or capsid o What is a gene?
Unit of genetics information
Genes code for proteins(also tRNA & rRNA)(not every rna translated into proteins)
In Bacteria 85-90% of the genome consists of coding sequence
In human only 1% of the genome is coding sequence o What is a chromosome?
IN eukaryotes is a long stretch of DNA associated with proteins
Chromosomes contain genes and non-genic regions
Chromosomes are visible during mitosis or meiosis
Every gene is localized in a specific position along the chromosome called Locus o Genes and genomes sequences are available in public databases
Most commonly used
National Center for BIotechnolofy Information (NCBI)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
o How many types of chromosomes
Middle/Metacentric
Between Middle and End/Submetacentric
Close to end/ Acrocentric(parm=short/qarm=long)
At end/Telocentric o Karyotype
Decription of the complete set of the chromosomes of an organism
Chromosome arranged in a standard format showing
Number
Size
Shape o Homologous chromosomes
In pairs in diploid organisms
Same length
Same centromere location
Same genes in the same order
Exception: Sex Chromosomes o How man chromosomes organisms have
Number of chromosomes varies between species o Humans have 46 chromosomes o Chromosomes are in pairs: 2x23 o Haploid #(n) 23 o Diploid #(2n) 46
Ploidy: number of sets of chromosomes
Humans are diploid(2n;2sets)
Gemets are haploid(n;1set)
Yeast is a haploid(n) most of its life cycle
Many plats are polypoid; o Triploid(3n) o Tetraploid(4n) o What is an allele? o Pentaploid(5n)
One of the alternative forms of a gene
Diifrent alleles arise by DNA sequence mutation
Alleles go in pais(diploid organism)
For every Gene(locus there are 2 alleles, One of each homologous chromosome.
The pair of alleles for a gene = genotype(AA,Aa,aa)
The detectable appearance of a charater = Phenotype(ex. Seed color)
Dominant allele A: determines the phenotype
Recessive allele a: it does not show as phenotype if A present
Homozygote = identical
Heterozygote= different
Wild type: the allele most frequently observed in nature o The wild-type allele can be indicate with + o The mutant allele with intials of the mutation o Characters determined by one gene = monogenic traits o Characters determined by more than one gene = polygenic traits
# genes are known to control eye color in humans(more genes are involved but still unknown)
Skin color
Multiple genes(loci) contribute to skin color
Genes encoding proteins involved in the biosynthesis of malanine
Mitosis/Meiosis/Gametogenisis
o Two type of cell divison processes in eukaryotic cells(Mitosis/Meiosis) o Mitosis(2 2n cells) o Meiosis(4 n cells)
o The Cell Cycle an extended period between cell division, DNA synthesis, and chromosome replication phase
M phased (mitotic phase)
Nuclear and cell division
Phase checkpoints: key transition points
G1/S checkpoint
G2/M checkpoint
Spindle assembly checkpoint
Cytokinesis
S phase/dna replication
G0/ wont divide anymore
Interphase cell wont grow anymore
Apoptosis/ protection against cancerous cells; cell suicide o M Phase
Mitosis: separation of sister chromatids
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase- line up
Anaphase-pulled away opposite polls
Telophase- cytoplasm is seprated
Cytokinesis: separation of cytoplasm