Classification of Matter Achievement Scale 11
advertisement

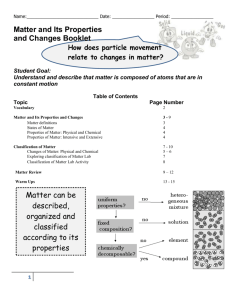
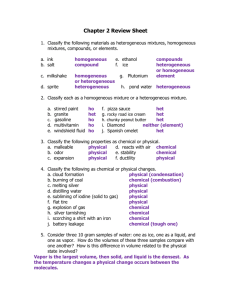
Unit 2- Classification of Matter I Can Statements: 1. I can classify matter based on its physical and chemical properties. A. Contrast and identify examples of chemical and physical properties of matter. (3.2) a. I can distinguish between extensive and intensive properties of matter. B. Contrast and identify examples of chemical and physical changes. (3.2) C. Contrast and identify pure substances and mixtures. (3.1) a. Based on chemical formulas, contrast and identify pure substances as either: a. Elements b. Compounds c. Molecules b. Based on various ways to separate mixtures, contrast and identify mixtures as either: a. Homogeneous b. Heterogeneous c. Contrast separation methods of mixtures (3.1) a. Chromatography b. Distillation c. Sorting d. Filtration e. Magnetism d. Define and identify examples of: a. Matter b. Pure Substance c. Atom d. Compound e. Molecule f. Mixture g. Homogeneous Mixture h. Solution i. Heterogeneous Mixture 2. I can analyze density as a physical property of matter. (2.8) a. Calculate density using the density formula. b. Predict whether materials will float or sink based on their relative densities. c. Explain why density is not dependent on the amount of matter present 3. I can evaluate a set of measurement for the amount of error present. A. I can calculate percent error for a measurement when given the accepted value. B. I can evaluate an experiment to identify possible sources of error. i. instrumental error ii. procedural error iii. operator error Vocabulary: Solid Liquids Gasses Plasma Bose-Einstein Condensate Melting Boiling Condensing Evaporating Sublimation Freezing Vacuum Matter Atom Element Compound Molecule Pure Substance Mixture Heterogeneous mixture Homogeneous mixture Solution Physical Property Chemical Property Physical Change Chemical Change Intensive Property Extensive Property Chromatography Distillation Magnetism Filtration Sorting Density Percent Error Instrumental Error Procedural Error Operator Error Achievement Scale: Goal Chemical and Physical Properties C Level Can list examples of chemical and physical properties. B Level Can classify practical examples as chemical or physical properties. A Level Can explain why specific properties are physical or chemical. Chemical and Physical Changes Can list examples of chemical and physical changes. Can list examples of intensive and extensive properties. Can provide examples of various types of matter (ex. Element, compound, etc.) Can define key elements of the states of matter. Can classify practical examples as chemical or physical changes. Can classify practical examples as intensive or extensive properties. Can classify examples as specific types of matter. Can explain why specific changes in matter are physical or chemical. Can explain why specific properties are intensive or extensive. Can give reasoning as to why given types of matter are classified differently. Can explain key reasons different characteristics Intensive and Extensive Properties Classifying Matter States of Matter Can rank the states of matter based on energy Density Given the mass and volume, can calculate density. Error Can provide examples of errors in the laboratory. present and spacing between molecules Can calculate the mass or volume of a substance given density and mass or volume. Can specifically identify sources of error given a situation. of the states of matter. Can find the density if a substance using geometric calculations and water displacement and convert units of density. Can calculate % error for a given measurement and explain how that error might be fixed. Sample Questions: C Level: List two examples of intensive properties and two examples of extensive properties. What is an example of a homogeneous mixture? What is the density of a material with a volume of 50mL and a mass of 200g? B Level: Classify carbon dioxide as an element, compound, homogeneous mixture, or heterogeneous mixture. A piece of zinc is dropped into hydrochloric acid and bubbles start to appear. What type of change is this? Is the property that causes this physical or chemical? Intensive or extensive? Gold has a density of 19.6 g/cm3. If the mass of a gold necklace is found to be 32.0g, what is the volume of the necklace in g? A Level: Air is usually classified as a homogeneous mixture. Explain a scenario that could cause a sample of air to become a heterogeneous mixture giving reasoning to support your answer. Classify copper’s property that it is a good conductor of heat as physical or chemical, as well as extensive or intensive and give reasoning to support your answer. Gold has a density of 19.6 g/cm3. If a gold necklace is dropped into a graduated cylinder containing 25.0mL of water and the water level rises to 29.5mL, what is the mass of the necklace in kg?