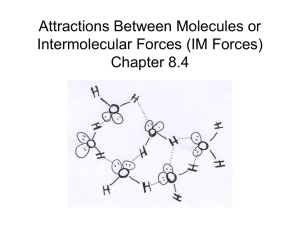
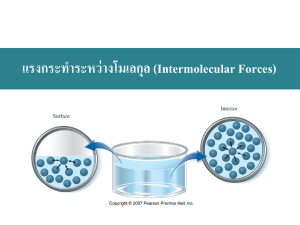
Intermolecular Forces Identify the strongest intermolecular force
advertisement

Intermolecular Forces Identify the strongest intermolecular force present in pure samples of the following substances: a. SO2 (polar) b. H2O (polar) c. CH2Cl2 (polar) d. SCO (polar) e. PCl3 (polar) f. SO3 (non-polar) 2. What are the four types of intermolecular forces (bonds)? 3. Which is the strongest of the four intermolecular forces (bonds)? 4. What is required for hydrogen bonding to be present? 5. What is the difference between ion-dipole and dipole-dipole? 6. Which intermolecular force is present in all matter? 7. Which intermolecular force is the weakest? 8. In the following pairs of substances, determine which will have the stronger London dispersion force? Show your reasoning for the selection. a. H2O or H2S b. CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH3 c. HI or HF 9. As the intermolecular forces increase, what happens to the boiling point or melting point of the substance? 10. When a phase change such as freezing or condensation occurs, what happens to intermolecular bonds? Are they formed or are they broken? 1. Intermolecular Forces Identify the strongest intermolecular force present in pure samples of the following substances: a. SO2 (polar) b. H2O (polar) c. CH2Cl2 (polar) d. SCO (polar) e. PCl3 (polar) f. SO3 (non-polar) 2. What are the four types of intermolecular forces (bonds)? 3. Which is the strongest of the four intermolecular forces (bonds)? 4. What is required for hydrogen bonding to be present? 5. What is the difference between ion-dipole and dipole-dipole? 6. Which intermolecular force is present in all matter? 7. Which intermolecular force is the weakest? 8. In the following pairs of substances, determine which will have the stronger London dispersion force? Show your reasoning for the selection. d. H2O or H2S e. CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH3 f. HI or HF 9. As the intermolecular forces increase, what happens to the boiling point or melting point of the substance? 10. When a phase change such as freezing or condensation occurs, what happens to intermolecular bonds? Are they formed or are they broken? 1. Intermolecular Forces 1. Identify the strongest intermolecular force present in pure samples of the following substances: a. SO2 (polar) b. H2O (polar) c. CH2Cl2 (polar) d. SCO (polar) e. PCl3 (polar) f. SO3 (non-polar) 2. What are the four types of intermolecular forces (bonds)? 3. Which is the strongest of the four intermolecular forces (bonds)? 4. What is required for hydrogen bonding to be present? 5. What is the difference between ion-dipole and dipole-dipole? 6. Which intermolecular force is present in all matter? 7. Which intermolecular force is the weakest? 8. In the following pairs of substances, determine which will have the stronger London dispersion force? Show your reasoning for the selection. g. H2O or H2S h. CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH3 i. HI or HF 9. As the intermolecular forces increase, what happens to the boiling point or melting point of the substance? 10. When a phase change such as freezing or condensation occurs, what happens to intermolecular bonds? Are they formed or are they broken?