Intermolecular Forces
advertisement
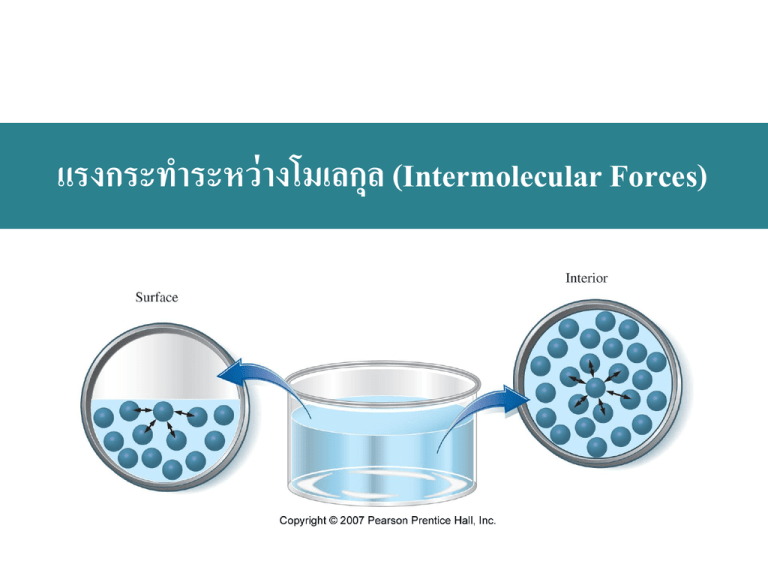
แรงกระทำระหว่ ำงโมเลกุล (Intermolecular Forces) เนือ้ หำทีจ่ ะเรียน 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Intermolecular Forces and some Properties of Liquids Vaporization of Liquids: Vapor Pressure Some Properties of Solids Phase Diagrams Van der Waals Forces Hydrogen Bonding Network Covalent Solids and Ionic Solids Intermolecular Forces and Some Properties of Liquids Cohesive Forces Intermolecular forces between like molecules. Adhesive Forces Intermolecular forces between unlike molecules. Surface Tension Energy or work required to increase the surface area of a liquid. Viscosity A liquids resistance to flow Intermolecular Forces Intermolecular Forces Vaporization of Liquids: Vapor Pressure ΔHvap = Hvapor – Hliquid = - ΔHcondensation Boiling Point Mercury manometer Vapor pressure of liquid Pvap independent of Vliq Pvap Pvap independent dependent on of Vgas T Vapor Pressure and Boiling Point Vapor Boils at Low Pressure The Critical Point •ความหนาแน่นของของเหลวลดลงแต่ของไอจะเพิ่มขึ้นและต่อมาจะมีค่าเท่ากัน •แรงตึงผิวของของเหลวจะเข้าใกล้ศนู ย์ ชั้นของของเหลวและไอจะกลายเป็ นหนึ่ งเดียว ไม่เห็นความแตกต่าง ตัวอย่ ำงกำรใช้ ข้อมูลควำมดันไอ จากปฏิกิริยาเคมีชนิดหนึ่งได้ผลิตภัณฑ์เป็ นน้ ามวล 0.132 g ที่อุณหภูมิ 50.0 oC ในภาชนะปิ ดปริ มาตร 525 mL จงทานายว่าน้ านี้จะอยูใ่ นสถานะ (a) liquid only (b) vapor only (c) liquid-vapor equilibrium Clausius-Clapeyron Equation ln P = -A ( 1 )+B T ΔHvap A= R ln ΔHvap P2 1 =( P1 T R 1 1 ) T2 Some Properties of Solids Freezing Point Melting Point ΔHfus(H2O) = +6.01 kJ/mol Sublimation ΔHsub = ΔHfus + ΔHvap = -ΔHdeposition Phase Diagrams Iodine Phase Diagrams Carbon dioxide Supercritical Fluids Decaffeination with Supercritical CO2 Water Interpreting a Phase Diagram Slide 24 of 54 General Chemistry: Chapter 12 Prentice-Hall © 2007 Van der Waals Forces Instantaneous dipoles. Electrons move in an orbital to cause a polarization. Induced dipoles. Electrons move in response to an outside force. Dispersion or London forces. Instantaneous dipole – induced dipole attraction. Related to polarizability. Phenomenon of Induction Instantaneous and Induced Dipoles < 10 kJ/mol Dipole Dipole Interactions 5 to 20 kJ/mol Electrostatic Potential Maps Slide 29 of 54 General Chemistry: Chapter 12 Prentice-Hall © 2007 ควำมสั มพันธ์ ระหว่ ำงแรงกระทำระหว่ ำงโมเลกุลกับสมบัตขิ อง สำรประกอบ เรี ยงลาดับจุดเดือดของสารต่อไปนี้: CCl4, Cl2, ClNO, N2. จุดเดือดที่พบจริ ง CCl4 = 349.9 K ClNO = 266.7 K Cl2 = 239.1 K N2 = 77.3 K Hydrogen Bonding 15 to 40 kJ/mol Hydrogen Bonding Hydrogen Bonding in HF(g) Hydrogen Bonding in Water around a molecule in the solid in the liquid Other examples of H-Bonds DNA Double Helix The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Network Covalent Solids and Ionic Solids Other Carbon Allotropes Interionic Forces Energy Changes in the Formation of Ionic Crystals Ion-dipole Interactions cation-p Interactions anion-p Interactions p-p Interactions Hydrophobic Effects Focus On Liquid Crystals Liquid Crystal Thermometers End of Chapter Questions You can think about problems in reverse to help sort out a strategy. a b c If I had the answer, what would I have used to get it.