Fertilization
advertisement

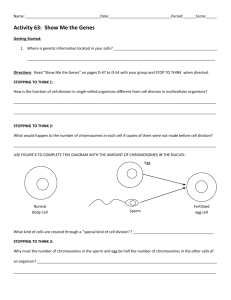
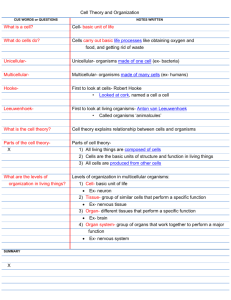
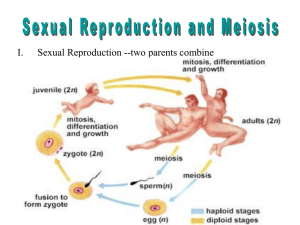
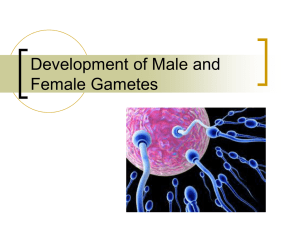
EOC Vocabulary Teacher Key Pages 81-94 1. Fertilization- Sperm and eggs unite within the mother’s reproductive system. 2. Gestation- Length of human development / how long the fetus is in the womb. Ex- humans is 9 months. 3. Embryo- The earliest stage of development, first eight weeks of pregnancy the baby is considered this. 4. Fetus- the 8th week until birth, a developing human. 5. Implantation- When the fertilized egg becomes implanted into the uterine wall of the uterus. 6. Placenta- structure through which the mother nourishes the embryo with nutrients. Also known as the afterbirth. 7. Zygote- fertilized egg 8. Uterus- provides protection and nourishment during development. 9. Amnion- encloses and protects the embryo. Later develops into the amniotic sac. 10. Chorion- Interacts with the uterus to form the placenta. 11. Acrosome- Releases enzymes that allow the sperm to penetrate the egg’s membrane. 12. Gap 1- rapid cell growth during this stage of Interphase, 90% of its time is spent here. 13. Synthesis- DNA is copied and the end result is two chromatids. 14. Gap 2- final stage of Interphase before mitosis where final preparations to divide are made. 15. Mitosis- Nucleus of the cell is divided into two identical daughter cells. 16. Cytokinesis- cytoplasm divides. 17. Homeostasis- Maintaining a stable internal balance. Ex- normal body temp or pH. 18. Prophase- Chromosomes coil up and become visible, nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindles form. 19. Metaphase- Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and align for cell division. 20. Anaphase- Centromeres divide and chromatids move apart to opposite sides of the cell. 21. Telophase- Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes shorten and uncoil, spindles dissolve, and Mitosis is complete starting the formation of identical daughter cells. 22. Cell Cycle- Repeating sequence of cellular growth and division during the life of an organism. 23. Asexual Reproduction- Reproduction involving one parent and the offspring are genetically identical to the parent. 24. Sexual Reproduction- Reproduction involving two parents and the offspring are genetically different to the parents. 25. Gametes- Sex cells, sperm and eggs. 26. Haploid Cells- Contains one set of chromosomes. Ex- 23 or n. 27. Binary Fission- One cell turns into two and it continues to rapidly divide / double. Ex.- bactieria. 28. Budding- New individuals split off from existing ones and create a new individual. Ex- Hydra 29. Fragmentation- The body breaks into several pieces and grows new individuals. Ex- sea star 30. Diploid- Cells have two copies of each chromosome one from mom and dad, totaling 46 or 2n 31. Independent Assortment- random distribution of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.