Development of Male and
Female Gametes
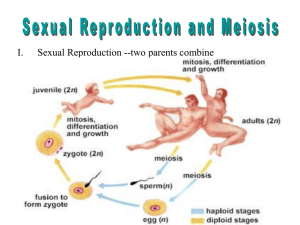
Gemetogensis
Formation of sex cells during meiosis
There are two forms:
Spermatogensis-occurs in testes
producing sperm
Oogenesis-occurs in ovaries producing
eggs.
Oogenesis
Cytoplasm of the female
gametes does not divide
equally after each division
One daughter cell called an
ootid receives most of the
cytoplasm
Ootids are unfertilized eggs
Remaining 3 daughter cells
are called polar bodies
Oocye-cells that give rise to
egg cells.
Oogenesis
Polar bodies- are cells produced during meiosis that
contain all the genetic information of a haploid egg
cell but lack sufficient cytoplasm to survive.
Polar bodies can not be fertilized and die, and their
nutrients get absorbed in the body
Only one egg cell is produced
The egg requires nutrients and organelles in its
cytoplasm therefore when it gets fertilized it has fuel
for cell division.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatocytes- cells
that give rise to sperm.
Sperm cells
Show equal division of
cytoplasm
Less cytoplast than egg
cells and have a short
life span
Develop a flagella and
is streamlined
Designed for movement
Sperm vs. Eggs
Males make more sex cells than females
Males can produce 1 billion sperm a day
Females are born with 400 000 eggs cells
and only 400 ever mature
Oocyes does not divide after a women
reaches puberty.
Women ages increase=#of eggs decreases
Between the ages of 50 and 60 there are no
eggs in the ovary=menopause
Karyotype
Is an organized profile
of an individuals
chromosomes.
Chromosomes are
arranged and
numbered by size, from
largest to smallest.
Each pair of
chromosomes appears
to have its own “bar
code” of characteristic
bands
Sex Chromosomes
The last pair of chromosomes form males
and females are different
These are the sex chromosomes =pair of
chromosomes that determine the sex of an
individual
Autosomes-are chromosomes not involved
with sex determination
Rod shaped= x chromosome
Hook shaped= y chromosome
MALE (XY)
FEMALE (XX)
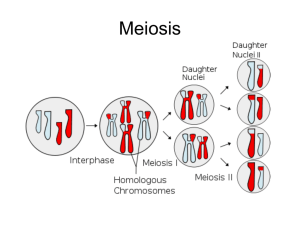
Nondisjunction
• Occurs when 2 homologous chromosomes move to the
same pole during meiosis I or when 2 chromatids do not
separate during meiosis II
• Produces gametes with 22 or 24 chromosomes
• Results in too much or too little genetic information.
Nondisjunction
Trisomy- 24 + 23 = zygote with 47
chromosomes. End up with 3 homologous
chromosomes in every cell of an organism.
Monosomy- 22 + 23 = zygote with 45
chromosomes. There is a single
chromosomes. There is a single
chromosome in place of a homologous pair
Down Syndrome
Trisomic disorder
Zygote receives 3 homologous
chromosomes for the chromosome
pair #21
This disorder can show a wide range
of mental abilities
1 in 600 babies
Risk of having a baby with age.
Turners Syndrome
Monosomic disorder in which a
female has a single X chromosome.
In the egg cell both X chromosomes
go to the same pole during meiosis I
Egg with no X gets fertilized by a nrmal
sperm.
1 in every 3000 female babies
Do not develop sexually
Klinefelters Syndrome
Nondisjunction in either sperm or egg
Trisomic disorder in which a male carries
an XXY condition
Male at birth
At puberty he produces high levels of female
sex hormones
Sterile
1 in every 500 male births
Homework
Find me another nondisjunction
disorder and provide details about it.