I.
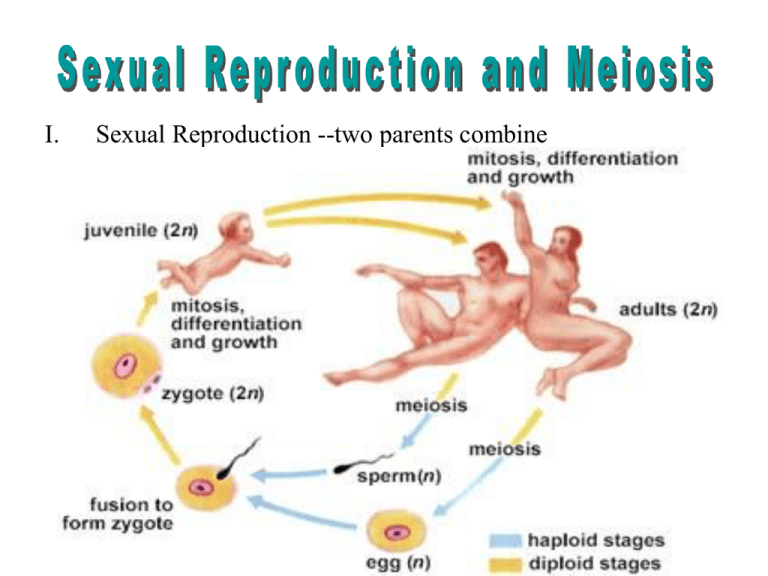
Sexual Reproduction --two parents combine
1. The sex cell from the male parent is sperm.
a. Sperm head is almost all nucleus (genetic info)
Gametes: Sex Cells
2. The sex cell from the female parent is the egg
a. Eggs are large and contain food material.
Diploid / Haploid
•Cells that have 2 sets of DNA are
diploid.
• Diploid is 2n.
• All of your body cells are 2n
•A sex cell with one set of
DNA is haploid.
• Haploid is n
• sperm & egg (gametes)
are haploid
Fertilization-- joining of egg and sperm
•n + n = 2n or 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes
(23 chromosomes from your dad join with 23
chromosomes from your mom (n=23).)
• fertilization forms a zygote
- grows to become an embryo
by mitosis
•The zygote has the diploid (2n = 46) chromosome
number for that organism.
•The zygote (or 1st body cell) does mitosis to
grow and develop.
Stages of Meiosis
Prophase I 1. double stranded chromosome and spindle fibers
appear.
2. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
3. Tetrads form (4 chromatids).
4. Crossing over occurs.
Metaphase I - The pairs of chromosomes (tetrads)
line up in the center of the cell.
Anaphase I - double stranded chromosomes (tetrad)
separate from its twin. Each one is pulled to
opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase I - The cytoplasm divides and two cells
form. Each chromosome is still double stranded.
NOT FOLLOWED BY INTERPHASE!
Prophase II - the double stranded
chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each
new cell.
Metaphase II - the double stranded chromosomes
move to the center of the cell:
Anaphase II - The centromere divides and the
chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of
the cell.
Telophase II - the spindle fibers disappear and
a nuclear membrane forms around the
chromosomes at each end of the cell.
- followed by cytokinesis II
Meiosis Animation
Meiosis
(sperm)
(egg)
III. The Importance of Sex Chromosomes
A. Body cells have chromosomes that are found in pairs
B. The 46 human chromosomes form 23 pairs of chromosomes
C. The pairs form because the chromosomes are alike
The 23rd pair
determines the sex or
gender of the child.
XX= female
XY= male