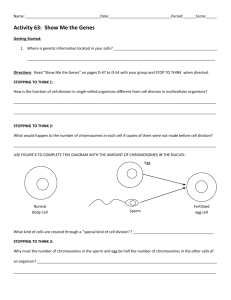
(pg 103) On an index card, create and solve the Punnett square for
advertisement
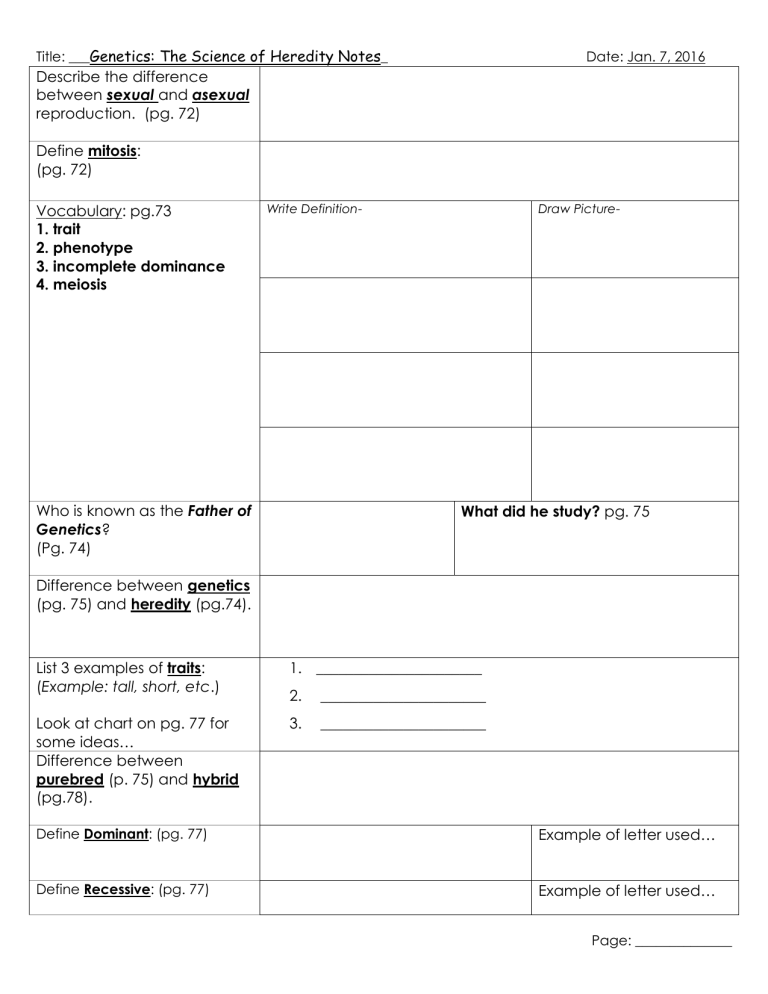
Title: ___Genetics: The Science of Heredity Notes_ Date: Jan. 7, 2016 Describe the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. (pg. 72) Define mitosis: (pg. 72) Vocabulary: pg.73 1. trait 2. phenotype 3. incomplete dominance 4. meiosis Write Definition- Who is known as the Father of Genetics? (Pg. 74) Draw Picture- What did he study? pg. 75 Difference between genetics (pg. 75) and heredity (pg.74). List 3 examples of traits: (Example: tall, short, etc.) 1. ______________________ 2. ______________________ Look at chart on pg. 77 for some ideas… Difference between purebred (p. 75) and hybrid (pg.78). 3. ______________________ Define Dominant: (pg. 77) Example of letter used… Define Recessive: (pg. 77) Example of letter used… Page: ______________ Title: ___Genetics: The Science of Heredity Notes_ Date: Jan. 7, 2016 Define Probability: (pg. 81) What is this diagram called and what is it used for? (pg. 82) Name… Used for… Define phenotype: Example of Phenotype: Define genotype: Example of Genotype: Define: Example of letter combination: Difference between phenotype and genotype. (pg. 84) Homozygous (pg. 84) Homo=same 1. ___________ 2. ____________ Heterozygous (pg. 84) Define: Hetero=different Punnett Square Practice: (pg. 82-83) Example of letter combination: 1. ____________ Complete- Example: Page: ______________ Title: ___Genetics: The Science of Heredity Notes_ Date: Jan. 7, 2016 Codominance Example Most traits are the result of complex patterns of inheritance. (pg. 86) Four complex patterns of inheritance are described in this lesson. Name of pattern: Describe pattern of inheritance: 1. __________________ (pg. 87) 2. __________________ (pg. 87) 3. __________________ (pg. 88) 4. __________________ (pg. 88) Some traits are inherited, while others are acquired. Determine whether each of these traits are inherited or acquired. (pg. 89) 1. height Read pg. 89-90 4. hedge shapes HINT-Inherited: carried by genes 2. dyed hair color 3. fish body color 5. freckles According to the chromosome theory of inheritance, ___________________________________________________________________ complete the missing part of the sentence(pg. 94) During sexual reproduction, each parent passes genes to his/her offspring. The process of MEIOSIS happens in the reproductive organs to make this possible. Each parent can only pass half the total number of chromosomes to his/her offspring. Define Body Cells: These are the “parent” cells and contain the total number chromosomes required for each organism. Define SEX CELLS and fill in the number of chromosomes in each parent’s sex cell. These are called HAPLOID cells. Define Sex Cells: (pg. 96) 1. Skunk- 50 chromosomes 2. Mosquito-6 chromosomes 3. Corn- 20 chromosomes 4. Shrimp-90 chromosomes 5. Grasshopper-24 chromosomes 6. Human-46 chromosomes Page: ______________ Title: ___Genetics: The Science of Heredity Notes_ Illustration of MEIOSIS: (pg. 96-97) Answer this question pg. 90 Circle the correct answer Date: Jan. 7, 2016 Only genetic changes in (sex cells passed to offspring. /or/ body cells) can be What does a genetic technologist do? (pg. 92) Define: (pg. 106) Gene: Heredity: Trait: Complete the following sentence using the words: traits, heredity, and genes Define: MUTATION pg. 119 Could be harmful or beneficial. ____________________ determine ___________________ which is our ___________________. Definition- Examples: 1. _____________ (pg. 118) 2. _____________ (pg. 120) 3. _____________ (pg. 120) 4. __CANCER___ (pg. 121) How is CANCER like weeds in a garden? (pg. 121) How is CANCER treated? (pg. 123) 1. _______________________________ 2. _______________________________ 3. _______________________________ EXTRA CREDIT PREDICT IT! Activity: (pg 103) On an index card, create and solve the Punnett square for the described scenario. Turn this in for extra credit by FRIDAY, 1/9. Page: ______________ Title: ___Genetics: The Science of Heredity Notes_ Date: Jan. 7, 2016 Page: ______________