Chp 10 Child Development Power Point
advertisement

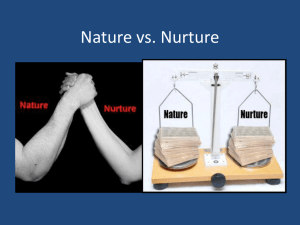
Chapter 10 Infancy and Childhood I. Heredity Versus Environment A. Nature v. Nurture controversy B. Nature – physical factors and heredity C. Nurture – the effects of environment D. Nature and nurture interaction in infants 1. 2 day old infants varied sucking patterns in response to their mothers voice suggests that a) They have memory, sounds are reinforcing and they learn from their environment. E. Genetics 1. Sperm contain 23 chromosomes 2. Egg contains 23 chromosomes 3. Zygote (fertilized egg) contains 46 chromosomes. 4. Chromosomes a. Contain genes that play a role in intelligence, activity level and response to a new stimuli. F. Twin studies 1. Dizygotic twins – fraternal twins a. 2 different sperm and eggs 1) Genetic make up is no different than any other two siblings 2. Monozygotic twins – identical twins a. Same sperm and egg, zygote splits 1) identical genes and heredity 3. Psychologists study twins thoroughly a. Especially when reared apart 1) They are very similar a) same fears and even nightmares as children, same jobs, same interests II. Developmental Patterns A. Family raised a chimp with their child 1. Chimp developed faster at first 2. Child passed up chimp at 2 years 3. This study shows that development within a species a. Is orderly and follows a specific timetable. B. Humans have a longer developmental period 1. Timing of development is different for each child. 2. Must integrate brains with body movements 3. Baby has automatic reflexes with control. C. Maturational processes 1. Child is preprogrammed for certain activities like walking (can’t teach them) a. Even if they never practice they will eventually walk normally. 2. Maturation is the automatic, orderly, and sequential process of physical and mental development. D. Growth Cycles 1. Some developmental areas develop more rapidly or slowly 2. At age 8 – 95% of the basic structure of the brain has developed a. but the body has 55% developed b. reproductive system is 90% undeveloped 3. Growth cycle for girls is more orderly and stable than boys. E. Critical Periods 1. Definition a. A specific time period in an animal’s maturation when a skill may be learned, if it is not learned it will never occur. 2. Imprinting –Conrad Lorenz a. Imprinting is a critical period b. Ducks and some other birds are programmed to accept a mother figure at a certain time. 1) It is a result of chemical being released at a certain time. a) if an animal’s chemistry is altered, the critical period can be extended or eliminated. 3. Dogs critical period a. attachments up to 12 weeks. 1) afterwards they are unpredictable. 4. Babies critical period a. 1st month – smile without learning b. 2nd month – smiles as a response to sounds. 1) blind children do also, therefore is not learned. 5. Animals and humans critical period a. Need touching, holding from birth 1) if not the result is disastrous 2) A young girl named Genie was locked up without human contact for at least 5 years 6. Human critical period a. To learn foreign language with natural accent 1) Must learn before 12 years 2) a few people with a special ability will be more successful 7. Animals a. Must learn a particular skill during their critical period or it will never be learned. 8. Feral children miss critical periods a. Children supposedly raised by animals 1) one documented case a) Boy living in woods discovered at 11 b) could not speak, did not growl or act like an animal c) missed maturation of social settings d) had no human skills like speech and writing would not fully recover. III. The Family and Child Development A. Extended family a. Includes aunts, uncles, grandparents B. Nuclear family a. Parents and children C. Divorce rate – over 50% a. Before children reach 18 a. 50-60% will spend at least 1 year in a single parent family D. Step parents 1. Are often resented along with step siblings 2. Family should integrate slowly so that children get used to the new arrangement E. Income 1. Most families need more than one income 2. The women in most families work outside the home 3. Women still do most of the household chores even though they work F. Mothers working outside the home 1. Their children have the same level of attachment as those of home moms a. even thought they spend half the time with their children b. If moms like their job their relationship with their children is stronger G. Fathers 1. spend less time with their children but do the same things with them as moms 2. help children with their self esteem 3. When father is absent a. boys are just as masculine as boys living with their fathers b. do not get into more trouble c. have good self esteem if they are cared for properly. H. Parenting styles 1. Permissive a. Allow children to do whatever they want. b. Child does not learn what behavior is unacceptable 2. Authoritarian (dictatorial) a. Tyrants, rigid, inflexible, harsh b. Children with these parents are moody, have poor self esteem, no social skills 3. Authoritative a. Have authority, not a dictator b. flexible and caring I. Child Abuse ( 100,000s cases a year) 1. Discipline allows a child to grow psychologically 2. Slapping and hitting is not the best way to solve problems a. Does not teach right or wrong b. can get out of control and lead to child abuse. 3. Why would a parent abuse a child? a. Don’t know much about children b. Not mature themselves 1. Looks for love from a baby rather than the responsibility c. Come from a violent or abusive background d. Financial problems and isolation e. Unemployment f. Stress, alcoholism, psychological problems. g. Teenage parents IV Sequences of Development A. Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development 1. The way a child’s thinking and reasoning change and grow. 2. See handout B. Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development 1. The development of ideas about right and wrong s. See handout