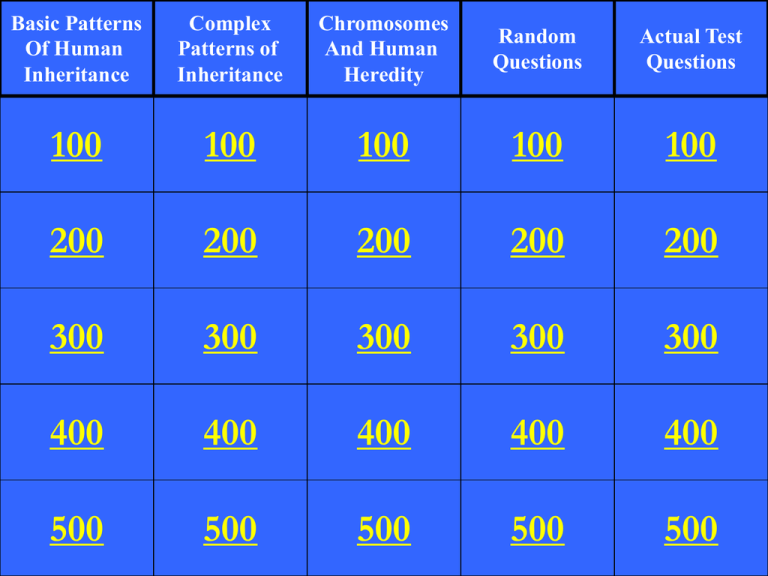
Basic Patterns
Of Human
Inheritance
Complex
Patterns of
Inheritance
Chromosomes
And Human
Heredity
Random
Questions
Actual Test
Questions
100
100
100
100
100
200
200
200
200
200
300
300
300
300
300
400
400
400
400
400
500
500
500
500
500
The name of the recessive genetic
disorder that causes excessive
mucus production in the lungs
Cystic Fibrosis
The name of the dominant
genetic disorder that results in
short arms and legs with a large
head
Achondroplasia
A diagram that traces the
inheritance of a particular trait
through several generations
Pedigree
An individual who is
heterozygous for a recessive
disorder
Carrier
The name of the recessive genetic
disorder that causes mental
disabilities, an enlarged liver, and
kidney failure
Galactosemia
The type of inheritance in which
the heterozygous phenotype is an
intermediate phenotype
Incomplete Dominance
The type of inheritance in which
humans inherit blood type and
rabbits inherit coat color
Multiple Alleles
The type of inheritance in which
both alleles are expressed in the
heterozygous condition
Codominance
Traits controlled by genes located
on the X chromosome
Sex-linked traits
Skin color is inherited through
this type of inheritance
Polygenic Inheritance
A micrograph that consists of
pairs of homologous
chromosomes arranged in
decreasing size
Karyotype
Protective caps found on the end
of chromosomes
Telomeres
The process during which sister
chromatids fail to separate during
meiosis
Nondisjunction
The human condition in which a
person has 3 of the number 21
chromosome
Down Syndrome
The human condition in which
the person has 2 X chromosomes
and a Y chromosome
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
A recessive genetic disorder in
which the person would have no
color in the skin, eyes, and hair
Albinism
The 22 pairs of chromosomes in
your body that are NOT sex
chromosomes
Autosomes
The name of the sex linked
disorder characterized by delayed
blood clotting
Hemophilia
What blood type(s) can a person
receive if they are O-
O-
In order, name the two types of
inheritance:
1. Red, White, and Pink
Snapdragons
2. Coat Color in Labs
Multiple Alleles
Epistasis
A phenotype that results from a
dominant allele must have at least
_____ dominant allele(s) present
in the parent(s).
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
a. one
A man heterozygous for blood
type A marries a woman
heterozygous for blood type B.
The chance that their first child
will have type O blood is _____.
a. 0%
b. 25%
c. 50%
d. 75%
b. 25%
A person has a non-normal set of
sex chromosomes but is
obviously female. Her cells
show two Barr bodies. Which
condition accounts for these
observations?
a.XXX b. XXY
c. XYY d. XO
a. XXX
What part of a chromosome
might be involved with processes
such as aging and cancer?
a. karyotype
b. nondisjunction
c. telomere
d. telophase
c. telomere
A man’s grandfather on his
father’s side had galactosemia.
Assuming that his mother was
not a carrier, what is the
probability that this man is a
carrier for the disorder?
a. 0.25 c. 0.75
b. 0.50 d. 1.00
b. 0.50


![[11.1,11.2,11.3] COMPLEX INHERITANCE and HUMAN HEREDITY](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006715925_1-acaa49140d3a16b1dba9cf6c1a80e789-300x300.png)