2014 Yr10 Biology – Unit test 2
advertisement
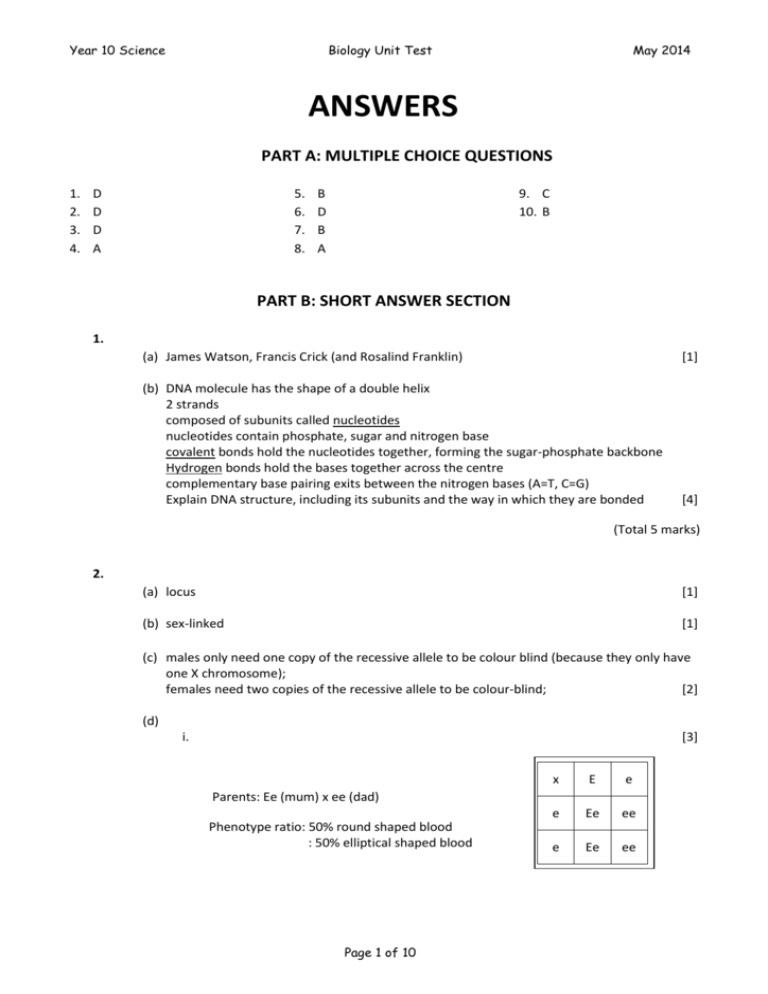
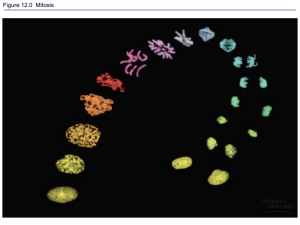
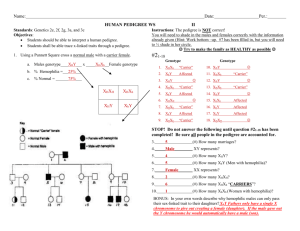
Year 10 Science Biology Unit Test May 2014 ANSWERS PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. D D D A 5. 6. 7. 8. B D B A 9. C 10. B PART B: SHORT ANSWER SECTION 1. (a) James Watson, Francis Crick (and Rosalind Franklin) [1] (b) DNA molecule has the shape of a double helix 2 strands composed of subunits called nucleotides nucleotides contain phosphate, sugar and nitrogen base covalent bonds hold the nucleotides together, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone Hydrogen bonds hold the bases together across the centre complementary base pairing exits between the nitrogen bases (A=T, C=G) Explain DNA structure, including its subunits and the way in which they are bonded [4] (Total 5 marks) 2. (a) locus [1] (b) sex-linked [1] (c) males only need one copy of the recessive allele to be colour blind (because they only have one X chromosome); females need two copies of the recessive allele to be colour-blind; [2] (d) i. [3] x E e e Ee ee e Ee ee Parents: Ee (mum) x ee (dad) Phenotype ratio: 50% round shaped blood : 50% elliptical shaped blood Page 1 of 10 Year 10 Science Biology Unit Test ii. iii. I II May 2014 Work out the possible phenotype for this child with regards to colour-blindness. Remember to use correct symbols and show all necessary working. [3] XC Xc Parents: XCXc (mum) x XCY (dad) x Phenotype ratio: 50% normal females : 25% normal males : 25% colour blind males XC X CX C X CX c Y XC Y Xc Y Key (1 mark), correct structure (1 mark), genotypes (1 mark) XcY ? ? [3] ? XCY XC Xc ? III (Total 13 marks) 3. (a) A heterozygote for a disorder – can pass it on without any symptoms themselves [1] (b) 2 [1] (c) [3] Key: H = normal, h = haem x Parents: XHXh (mum) x XHY (dad) Phenotype ratio: 50% normal female : 25% normal male : 25% haemophiliac male XH Xh XH XHXH XHXh Y XHY XhY (Total 5 marks) Page 2 of 10 Year 10 Science Biology Unit Test May 2014 4. (a) meiosis [1] (b) Phases: 2 (meiosis) and 1 (mitosis) Parent cell: reproductive cell (meiosis) and body cell (mitosis) Daughter cells: 4 (meiosis) and 2 (mitosis) Daughter cells: gametes (meiosis) and body cells (mitosis) Daughter cells: haploid (meiosis) and diploid (mitosis) Chromosomes in daughter cells: 23 (meiosis) and 46 (mitosis) [3] (c) Change in DNA sequence caused spontaneously or by environmental factors (d) Increased mutation increased variation [3] More variation allows for more competition and natural selection better suited organisms survive struggle Species begins to change over time as adaptations accumulate and increase in frequency (Total 6 marks) 5. (a) Divergent evolution [1] (b) DNA analysis Comparative embryology or anatomy Check if they can still mate to produce viable offspring Any other acceptable answer [2] (c) Variation existed geographical isolation occurred due to continental drift restricted gene flow between two groups of snakes different selection pressures acted on each group natural selection occurs different adaptations result in each group until they can no longer interbreed to produce viable offspring [4] (Total 7 marks) 6. (a) chimpanzee [1] (b) red kangaroo [1] (c) number of differences = estimation of time since the two species shared a common ancestor chimpanzee and human share a more recent common ancestor than the red kangaroo and human [2] (Total 4 marks) Page 3 of 10