Human Pedigree Activity 2
advertisement
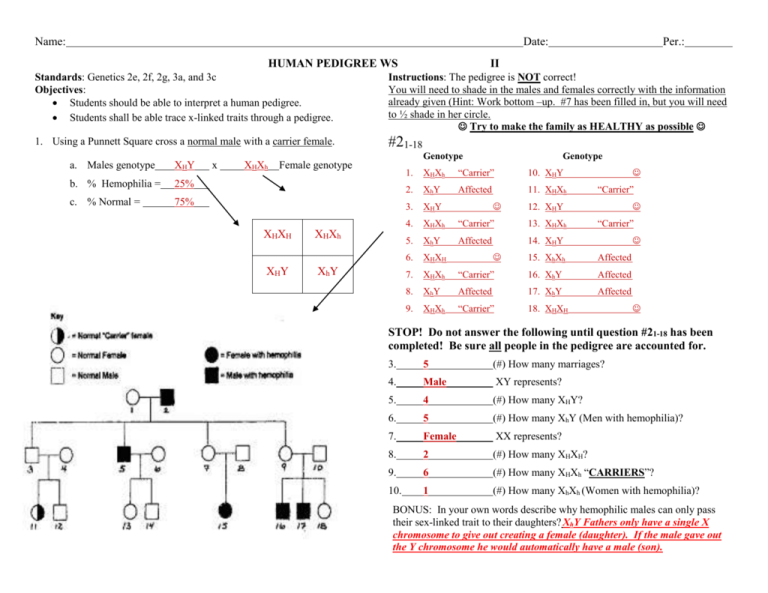
Name: Date: HUMAN PEDIGREE WS Per.: II Standards: Genetics 2e, 2f, 2g, 3a, and 3c Objectives: Students should be able to interpret a human pedigree. Students shall be able trace x-linked traits through a pedigree. Instructions: The pedigree is NOT correct! You will need to shade in the males and females correctly with the information already given (Hint: Work bottom –up. #7 has been filled in, but you will need to ½ shade in her circle. Try to make the family as HEALTHY as possible 1. Using a Punnett Square cross a normal male with a carrier female. #21-18 a. Males genotype XHY b. % Hemophilia = 25% c. % Normal = 75% x XHXh Genotype Female genotype XHXH XHXh XHY XhY Genotype 1. X HX h “Carrier” 10. XHY 2. XhY Affected 11. XHXh 3. X HY 4. X HX h “Carrier” 13. XHXh 5. XhY Affected 14. XHY 6. X HX H 7. X HX h 8. 9. “Carrier” 12. XHY “Carrier” 15. XhXh Affected “Carrier” 16. XhY Affected XhY Affected 17. XhY Affected X HX h “Carrier” 18. XHXH STOP! Do not answer the following until question #21-18 has been completed! Be sure all people in the pedigree are accounted for. 3. 5 (#) How many marriages? 4. Male XY represents? 5. 4 (#) How many XHY? 6. 5 (#) How many XhY (Men with hemophilia)? 7. Female XX represents? 8. 2 (#) How many XHXH? 9. 6 (#) How many XHXh “CARRIERS”? 10. 1 (#) How many XhXh (Women with hemophilia)? BONUS: In your own words describe why hemophilic males can only pass their sex-linked trait to their daughters? XhY Fathers only have a single X chromosome to give out creating a female (daughter). If the male gave out the Y chromosome he would automatically have a male (son).











