Geography 1-1c—Flashcard Terms and Definitions
General Geography Flash Card Definitions – Condensed
1—Overview of Geographic Terms
2—Mathematical Geography: A description of the earth using numbers and
measurements.
3—Universe: All of Heavenly Father’s and Jesus’ creations.
4—Galaxy: A very large group of stars and all matter surrounding them.
5— Solar System: The sun together with the planets and matter that are held by its
attraction and revolve around it.
6—The Earth’s Motion: How the earth moves in the solar system.
7—Orbit: The path the earth takes around the sun; it takes 1 year or 365 days to orbit
the sun once.
8—Seasons: One of the four quarters into which the year is divided by a particular
kind of weather; seasons are based on the position of the earth in its orbit
around the sun; winter, spring, summer, fall.
9—Axis: A central, straight, imaginary line about which the earth rotates; one
rotation equals 1 day or 24 hours.
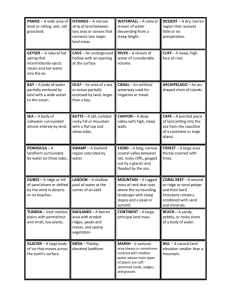
10—The Earth’s Surface and Measurements
11—Form: Shape of earth; earth is actually a sphere flattened along the axis from
pole to pole such that there is a bulge around the equator.
12—Dimension: The size of the earth.
13—Great Circles
14—Equator: The great horizontal circle of the earth that divides the earth into two
equal parts.
14a—Hemisphere: Half of a sphere or globe; one of the halves of the earth;
there are four hemispheres; northern, southern, eastern and western.
15—Prime Meridian: The meridian of 0 degrees longitude from which all other
longitude lines are measured.
16—Longitude Lines: Imaginary lines equally distant from the poles; longitude is
computed from 0-80 degrees East and West of the Prime Meridian at
Greenwich, England
17—Small Circles
18—Parallels/Latitude Line: Imaginary horizontal lines moving by degrees north and
south from the equator.
19—Climatic Circles/Tropics
TROPIC OF CANCER - The latitude line that is about 23 ½ degrees north of the
equator; the northernmost latitude reached by the overhead sun.
TROPIC OF CAPRICORN - The latitude line that is about 23 ½ degrees south of the
equator; the southernmost latitude reached by the overhead sun
20—Polar Circles: Either of the two parallels of latitude each at a distance from a
pole of the earth equal to about 23 degrees.
21—Time Zones: A region on the earth where the same standard time is used.
22—International Date Line: An imaginary line near the 180th meridian marked as
the place where each calendar day begins.
23—Poles: The ends of the axis of the earth.
© 2012 American Heritage Schools, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is hereby granted for copying of the notebook pages and other online resources for
use by the original purchaser’s own immediate family. No part of this publication may be transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Geography 1-1c—Flashcard Terms and Definitions
24—Globes and Maps
25—Physical Geography
26—Physical Composition of Earth (inside): What the inside of the earth is made of.
27—Crust: The outside layer of the earth; the thinnest layer; made mostly of rock, 3-34
miles.
28—Mantle: The thickest layer of the earth at about 1,800 miles; hottest layer; made
mostly of rock
29—Outer Core: Made of melted minerals, extremely hot, liquid.
30—Inner Core: Made of minerals, solid.
31—Natural Divisions of Earth
32—-Atmosphere: Entire mass of fluid, air, and vapors, surrounding the earth.
33—Climate: Average weather conditions over a period of years.
Weather: The condition of the atmosphere.
34—Temperature: Degree of hotness or coldness.
35—Wind: Movement of the air.
36—Breeze: Light wind on land or water.
37—Trade Winds: Winds that blow steadily from east to west and toward the equator
over most of the tropics.
38—Hurrican: A tropical storm with winds of 74 miles per hour or more.
39—Tornado: Violent destructive whirling wind.
40—Vapor/Humidity: Fine separated particles of water floating in and clouding the air.
41—Precipitation/Rain: Water falling in drops from the clouds.
42—Air Pressure: The force pressing on you by the weight of tiny particles of air.
43—Hydrosphere: The water contained on the earth.
44—Oceanic Waters: Waters found in the ocean.
45—Ocean: One of the four large bodies of salt water on the earth.
46—Wave: A moving ridge or swell on the surface of a body of water.
47—Current: A stream of water moving in a definite direction through the ocean; some
are warm, some are cold.
48—Bay: A body of water smaller than a gulf that is nearly surrounded by land.
49—Gulf: Extension of an ocean or a sea into the land.
50—Sea: A large body of water partly or completely enclosed by land.
51—Strait: A narrow stretch of water that connects two larger bodies of water.
52—Sound: A body of water separating one or more islands from the mainland.
53—Harbor: A sheltered place where ships may anchor safely.
54—Iceberg: A large floating mass of ice detached from a glacier.
55—Trench: A long, steep-sided, narrow depression in the ocean floor.
56—Coral Reef: A ridge of rock or sand at or near the surface of water.
57—Continental Shelf: A shallow underwater plain forming a border around a
continent, usually ending with a steep slope to the deep ocean floor.
58—Continental Waters: Waters found on the continent.
59—River/Stream: A large stream of water flowing through land.
60—Upstream: The direction from which a river flows.
61—Downstream: The direction toward which a river flows.
62—Source: The place where a river begins, usually in highlands.
63—Tributary: A river or stream that flows into a larger river.
64—Mouth: The place where a river flows into a larger body of water.
65—Delta: Land deposited at the mouth of a river.
© 2012 American Heritage Schools, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is hereby granted for copying of the notebook pages and other online resources for
use by the original purchaser’s own immediate family. No part of this publication may be transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Geography 1-1c—Flashcard Terms and Definitions
66—Lake: An inland body of water, smaller than a sea.
67—Fresh Water Lake: A lake which has water entering in and out of it.
68—Salt Water Lake: A lake which has water entering, but it has no outlet.
69—Channel: A deep, narrow body of water connecting two larger bodies of water;
the deeper part of a waterway.
70—Canal: A man-made ditch for transportation or irrigation.
71—Reservoir: A lake where water is stored for future use; sometimes formed by a dam.
72—Glacier: A large body of slowly moving ice.
73—Ice Sheet: A glacier forming on an extensive area of relatively level land and
flowing outward from its center.
74—Groundwater: The water found beneath the surface of the ground; the source of
water in springs and wells.
75—Water Plants: Water plants common to the area.
76—Water Animals: Water animals common to the area.
77—Lithosphere: The portion of the earth which is land.
78—Landforms: Land distinguished by its shape or form.
79—Continent: One of the seven large bodies of land on the earth.
80—Peninsula: A body of land almost surrounded by water.
81—Isthmus: A narrow strip of land that connects two larger bodies of land.
82—Cape: A point of land sticking out into a body of water.
83—Island: Land entirely surrounded by water, smaller than a continent.
84—Archipelago: A group of islands.
85—Fjord: A narrow inlet of the sea with steep banks made by a glacier.
86—Sea Coast: Land next to the sea.
87—Topography: Land distinguished by its elevation.
88—Mountain: High, rocky land, usually with steep sides and a pointed or rounded top,
higher than a hill.
89—Divide: A height of land that separates river basins.
90—Mountain Range: A group of mountains bordered by lowlands.
91—Volcano: A mountain formed of rock or ash thrown up from inside the earth.
92—Plateau: A region that is mostly high and flat.
93—Hill: A raised part of the earth’s surface, with sloping slides; smaller than a
mountain.
94—Plain: Broad, level land.
95—Valley: Low land between hills or mountains.
96—Basin: A region drained by a river; land largely enclosed by higher land.
97—Canyon: A deep, narrow valley with steep walls.
98—Cliff: A high, steep wall of rock.
99—Rift: A separation of the earth formed by an earthquake.
100—Land Plants: Land plants common to the area.
101—Land Animals: Land animals living common to the area.
102—Political Geography: The artificial divisions of the earth and its people.
103—Boundaries: Lines marking separation; borders.
104—Population: Number of people in a country, city or area.
105—No Card
106—Religion: Organized system of faith and worship.
107—Economics: The buying and selling of products and services.
108—Region: A subdivision within a country or continent.
© 2012 American Heritage Schools, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is hereby granted for copying of the notebook pages and other online resources for
use by the original purchaser’s own immediate family. No part of this publication may be transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Geography 1-1c—Flashcard Terms and Definitions
109—Countries and Capitals: A nation and its seat of government.
110—Form of Government: How a country is ruled.
111—Major Languages: The most common forms of spoken communication in a nation.
112—Culture/Ethnography: A description of human culture.
© 2012 American Heritage Schools, Inc. All rights reserved. Permission is hereby granted for copying of the notebook pages and other online resources for
use by the original purchaser’s own immediate family. No part of this publication may be transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.