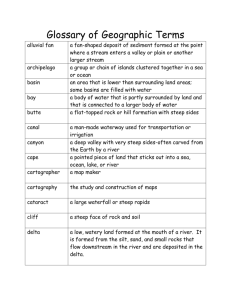
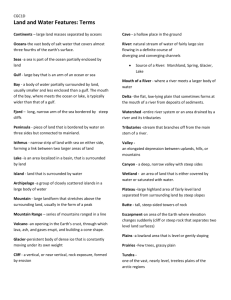
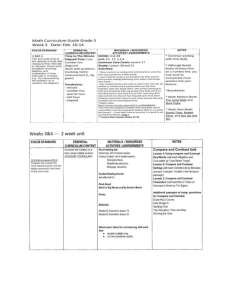
PRARIE * A wide area of level or rolling, wet, tall grassland
advertisement

PRARIE – A wide area of level or rolling, wet, tall grassland. ISTHMUS – A narrow strip of land between two seas or oceans that connects two larger land areas. WATERFALL – A natural stream of water descending from a steep height. DESSERT – A dry, barren region that receives little or no precipitation. GEYSER – A natural hot spring that intermittently ejects steam and hot water into the air. CAVE – An underground hollow with an opening at the surface. RIVER – A stream of water of considerable volume. CLIFF – A steep, high face of rock. BAY – A body of water partially enclosed by land with a wide outlet to the ocean. GULF – An area of a sea or ocean partially enclosed by land; larger than a bay. CANAL – An artificial waterway used for irrigation or travel. ARCHIPELAGO – An arcshaped chain of islands. SEA – A body of saltwater surrounded almost entirely by land. BUTTE – A tall, isolated rocky hill or mountain with a flat top and steep sides. CANYON – A deep valley with high, steep walls. CAPE – A pointed piece of land jetting into the sea from the coastline of a continent or large island. PENINSULA – A landform surrounded by water on three sides. SWAMP – A lowland region saturated by water. FJORD – A long, narrow coastal valley between tall, rocky cliffs, gouged out by a glacier and flooded by the sea. FOREST – A large area thickly covered with trees. DUNES – A ridge or hill of sand blown or drifted by the wind in deserts or on beaches. LAGOON – A shallow pool of water at the center of an atoll. MOUNTAIN – A rugged mass of rock that rises above the surrounding landscape with steep slopes and a peak or summit. CORAL REEF – A mound or ridge or coral polyps and their hard limestone remains, combined with sand and minerals. TUNDRA – Vast treeless plains with permafrost and small, low plants. BADLANDS – A barren area with eroded ridges, peaks and mesas, and sparse vegetation. CONTINENT – A large, principal land mass. BEACH – A sandy, pebbly, or rocky shore of a body of water. GLACIER – A large body of ice that moves across the earth’s surface. MESA – Flattop, elevated landform. MARSH – A wetlands HILL – A natural land elevation smaller than a mountain. area always or sometimes covered with shallow water whose main types of plants are softstemmed reeds, sedges, and grasses ISLAND – A piece of land, smaller than a continent, completely surrounded by water. VALLEY – An elongated lowland between mountain ranges or hills; often has a river or stream running along the bottom. PLAIN – A large area of relatively flat or gently rolling land. CRATER – A bowlshaped depression in the earth or the funnelshaped opening of a volcano. DELTA – A triangular VOLCANO – An opening plain formed by the gravel, silt, sand, and clay deposited at a river’s mouth where it slows to meet another body of water. in the earth’s crust through which red-hot, melted rock, or magma rises to the surface from deep inside the earth and spills out as lava. ATOLL – A ring-shaped island formed by coral buildup on the rim of an underwater volcano. JUNGLE – Land covered by dense tropical vegetation. ICEBERG – A mass of floating ice that has broken away from a glacier. SOUND – A long, relatively wide body of water, larger than a channel or strait, that often connects larger bodies of water. RAINFOREST – A dense tropical evergreen forest with an annual rainfall of at least 100 inches. SAVANNA – An open grassland with widely spaced trees in a hot, seasonally dry climate. STRAIT – A relatively narrow waterway joining two larger bodies of water. PANHANDLE – A narrow projection of a larger territory, as in Florida, Texas, and Oklahoma. CHANNEL – The deepest part of a river harbor. OCEAN – The earth’s largest continuous stretches of saltwater. LAKE – A large island body of fresh or saltwater. PLATEAU - A very large, flat area of land that usually is higher than the land around it, with at least one steep slope.