Sexual & Asexual Reproduction: Types & Processes
advertisement
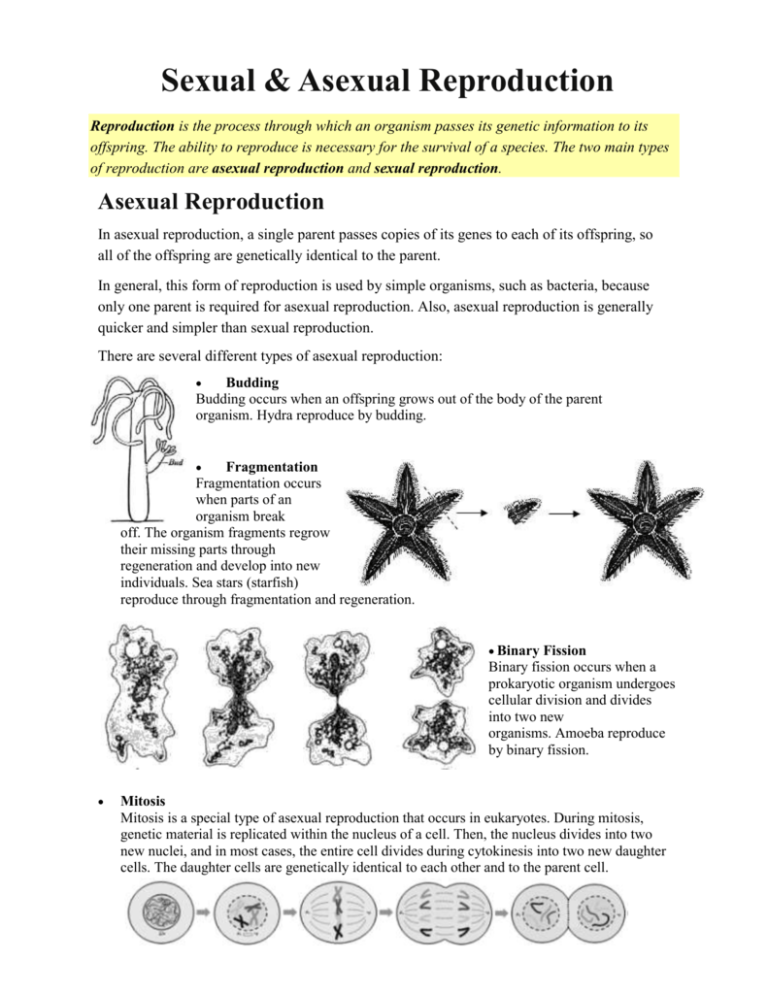
Sexual & Asexual Reproduction Reproduction is the process through which an organism passes its genetic information to its offspring. The ability to reproduce is necessary for the survival of a species. The two main types of reproduction are asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Asexual Reproduction In asexual reproduction, a single parent passes copies of its genes to each of its offspring, so all of the offspring are genetically identical to the parent. In general, this form of reproduction is used by simple organisms, such as bacteria, because only one parent is required for asexual reproduction. Also, asexual reproduction is generally quicker and simpler than sexual reproduction. There are several different types of asexual reproduction: Budding Budding occurs when an offspring grows out of the body of the parent organism. Hydra reproduce by budding. Fragmentation Fragmentation occurs when parts of an organism break off. The organism fragments regrow their missing parts through regeneration and develop into new individuals. Sea stars (starfish) reproduce through fragmentation and regeneration. Binary Fission Binary fission occurs when a prokaryotic organism undergoes cellular division and divides into two new organisms. Amoeba reproduce by binary fission. Mitosis Mitosis is a special type of asexual reproduction that occurs in eukaryotes. During mitosis, genetic material is replicated within the nucleus of a cell. Then, the nucleus divides into two new nuclei, and in most cases, the entire cell divides during cytokinesis into two new daughter cells. The daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. Sexual Reproduction In sexual reproduction, two parents each contribute genetic material to their offspring. Because both parents contribute genetic material, the offspring have traits of both parents, but they are not exactly like either parent. For sexual reproduction to occur, each parent must form a sex cell, also known as a gamete. Gametes are formed by meiosis. Meiosis is a two-step process of cell division that produces four cells that each contain half of the number of chromosomes present in the parent cell. A female gamete is called an egg, and a male gamete is called a sperm. When an egg's nucleus and a sperm's nucleus fuse, a fertilized egg, known as a zygote, forms. The zygote has the correct number of chromosomes for the species. This zygote then develops into a mature organism.