What Is Asexual Reproduction?
advertisement

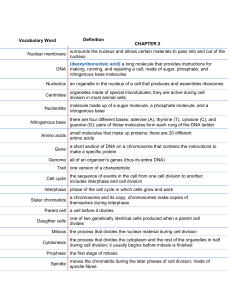
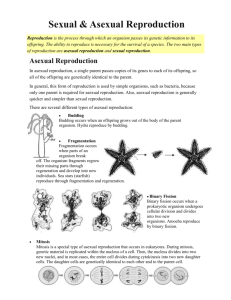
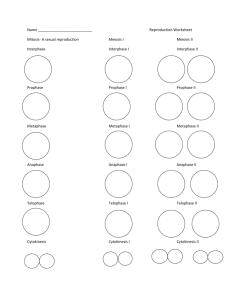
1 CHAPTER 4 LESSON 2 ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Key Concepts • What is asexual reproduction, and why is it beneficial? • How do the types of asexual reproduction differ? What Is Asexual Reproduction? • In asexual reproduction, one parent organism produces offspring without meiosis and fertilization. • Parent and offspring are genetically identical to each other. o Reason: Offspring inherit all of their DNA from one parent. 2 6 Types of Asexual Reproduction 1. Fission Recall: Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms. Their cells have a simpler cell structure than eukaryotes. o The DNA is not in a nucleus. Cell division in prokaryotes that forms two identical cells is called fission. A prokaryote’s DNA molecule is copied and each copy attaches to the cell membrane. The cell grows longer, pulling the two copies of DNA apart while the cell membrane begins to pinch inward along the middle of the cell. Then the cell splits and forms two new identical offspring. The original cell no longer exists. 3 Fission of E. coli bacterium: 2. Mitotic Cell Division One organism forms two genetically identical offspring through mitosis and cell division. Many unicellular eukaryotes reproduce in this way. Example - amoeba 4 3. Budding – p. 131 In budding, a new organism grows by mitosis and cell division on the body of its parent. The bud is the offspring. It is genetically identical to the parent. When the bud is large enough, it breaks off from the parent to live on its own. Example – The hydra. It is multicellular. 4. Animal Regeneration – p. 132 This occurs when an offspring grows from a piece of its parent. Examples of animals that can undergo regeneration: Some sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sponges, planarians Regeneration can produce new parts for salamanders, tadpoles, crabs, hydra 5 The human liver can regenerate to a degree. 5. Vegetative Reproduction – p. 133 • This is a form of asexual reproduction in which offspring grow from a part of a parent plant. • It usually involves structures such as the roots, the stems, and the leaves of plants. • Examples – spider plants, strawberry plants, mint plants, new potato plants from the eye of a potato 6. Cloning • Cloning is a type of asexual reproduction performed in a laboratory that produces identical individuals from a cell or from a cluster of cells taken from a multicellular organism. • Some plants can be cloned using a method called tissue culture. 6 • Animal cloning has been done. Example: Dolly the sheep. • Dolly developed arthritis and old age problems while still young. Dolly had to be “put down.” 7 Advantages of Asexual Reproduction • Organisms get to reproduce without a mate, saving time and energy. • Some organisms to produce large numbers of offspring in a short period of time. Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction • The results offer little genetic variation within the population. • Asexual reproduction can also be responsible for harmful genetic mutations.