Asexual Reproduction
advertisement

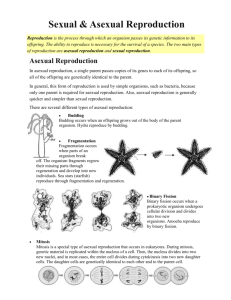
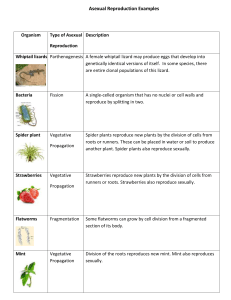
Asexual Reproduction Produces an offspring that is identical to the parent WHAT IS IT? Asexual reproduction usually happens very quickly. Large numbers of offspring are often produced. There are several types of asexual reproduction. Binary fission, budding,spore formation, regenerations and vegetative propagations. ADVANTAGES Rapid reproduction rates are possible. Only one organism is needed to reproduce. Works well for organisms that stay in one place, do not need to find a mate. Exact copy of parent Takes less energy/safe DISADVANTAGES Genetic variability is limited. Population is susceptible to massive extinction. Easier to overgrow resources, limiting factors. More difficult to adapt to environmental changes. TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Binary fission Budding Spores Regeneration Vegetative propagation Cloning BINARY FISSION This is the simplest form of asexual reproduction. The parent cell simply divides into two parts that are about equal. Each of the new cells, called daughter cells, becomes a separate individual. Each of the new offspring then grows to a normal size. Binary Fission is the usual method of reproduction of one celled organisms including protozoa, bacteria, and many algae. This is the process by which many multi-celled organisms grow. BUDDING New individual develop as small growths or buds on the surface of the parent organism. The new organism may break off and live independently or remain attached and live as a colony. Budding is different from binary fission because the offspring and parent are not the same size. Yeast, hydra, sponges and some worms reproduce by budding. Yeast and hydra can also reproduce sexually. SPORES Spores are special cells that some individual organisms produce. A thick, tough outer coating that protects the inner cell usually surround spores. When released by the parent, each spore may grow into a separate individual. Fungi, algae and protozoa can reproduce by spore formation. REGENERATION This is the ability to re-grow lost body parts. Starfish, earthworms, hydra and planarian can regenerate lost body parts. If a hydra is cut in half, each half can regenerate into a new individual. A planarian that is cut into several pieces will regenerate into several new worms. VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION This occurs when the new cells separate from the parent and form a complete independent individual. Plants can reproduce asexually be vegetative propagation. Plants also reproduce sexually by seeds. Roots, stems and leaves are called vegetative structures. Some plants reproduce vegetatively by special structures such as bulbs, corms, tubers, runners, and rhizomes. PARTHENOGENESIS Some animals may produce eggs that develop directly into offspring without fertilization. Common examples occur in insects, reptiles, and fishes. Often, these organisms may also reproduces sexually. The “choice” between sexual and asexual reproduction is typically mediated by environmental conditions. CLONING Cloning a a scientifically engineered reproductive technology that involves infusing the genetic material from a parent organism into and egg (nucleus removed) of another cell. Cell division is then stimulated using electrical current, which induces the cell to divide and develop in an embryo. The cloning of plants ensure that the new plants will be exact copies of the parent plant. Recently cloning technology was used to successfully clone a sheep—Dolly. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION GUIDE ORGANISM TYPE DESCRIPTION Whiptail lizards Parthenogenesis A female lizard may produce eggs that develop into genetically identical versions of itself. Bacteria Fission A single-celled organism that has no nuclei or cell walls and reproduce by splitting in two. Spider Plant Strawberries Vegetative Propagation Spider plants reproduce new plants by the division of cells from rot or runners. These can be place in water or soil to produce another plant. Spider plants and strawberries also reproduce sexually. Some flatworms Fragmentation Some flatworms can grow by cell division from a fragmented section of body. Blue-green algae Fission A single celled organism that reproduces by splitting in two. Hydra Budding Cell division forms a bud that is an identical copy of its single parent that separates from the parent and become independent. Sexual Reproduction Two parent cells join together to form offspring that are genetically different from the parents. Advantage Diversity among populations. ~ One disease won’t kill everyone. Disadvantage Two parent cells are necessary ~ Why is that a bad thing? - finding mates, energy, safety, etc Compare/Contrast Sexual Reproduction Advantage Asexual Reproduction Diversity in the population Disadvantage Two parent cells are necessary Why is that a bad thing? Advantage Fast, safe, many offspring, only one parent needed, EXACT copy of parent Disadvantage Not diverse, whole populations can be wiped out, can’t adapt well Examples: binary fission, budding, cloning, regeneration