Unit 3 – Evolution,
Heredity and Genetics
Read the “Cells that
Reproduce” article and
answer the questions
with a partner.
What questions will I be able to answer by
the end?
• How do I inherit my traits?
• What is the probability that my children will have
curly or straight hair?
• How does my body repair itself when I break a bone
or get a cut?
• How have ducks acquired webbed feet over time?
• Why are polar bears white?
• I have freckles but my sister doesn’t. How does this
happen?
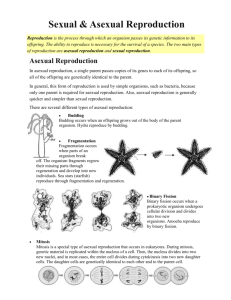
Asexual vs. Sexual
Reproduction
• Reproduction is the ability for
an organism to make more of
its kind.
• Cells come from other living cells.
• Cells reproduce (make more cells) by
dividing into two.
• This is called mitosis, and it is a form
of asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction-
one parent organism produces
two or more offspring that have
the same genetic material as the
parent.
• Low variation of offspring
Ex: Cell splits into two -->
Offspring – the “child” of a parent organism
How do organisms
reproduce asexually?
Small, unicellular organisms
undergo asexual
reproduction through cell
division (mitosis) and
budding.
Asexual reproduction: Cell division
This is an example of a
bacteria undergoing
cell division.
How many parents?
How many offspring?
Asexual reproduction – Cell division
This is a paramecium
undergoing cell
division.
How many parents?
How many offspring?
We have cell division going on in
our bodies too:
Our body cells go through cell
division for growth and repair:
• One bone cell divides to make 2
new bone cells (we grow taller
over time!)
• One skin cell divides to make 2 new
skin cells (we repair a cut in our skin)
How else do organisms
reproduce asexually?
Asexual Reproduction: Budding
This is a hydra. A new
organism is forming
on its side and can
live on its own once
it falls off.
How many parents?
How many offspring?
If small organisms and
cells undergo asexual
reproduction, how do
larger, more complex
organisms like humans
reproduce?
Sexual reproduction
•
•
•
•
Occurs in larger, complex organisms
Step 1: Meiosis creates gametes
Step 2: Gametes unite to form offspring (fertilization)
Gametes:
– Sperm cell (male)
– Egg cell (female)
• Involves 2 parents and one or many offspring.
• Produces high variation
Ex: human sperm fertilizes a human egg during sexual
intercourse and a new organism is formed.
homework
• Cut out the images given to you.
• determine which side of the chart they belong
on – asexual reproduction or sexual
reproduction.
• Fill in the blanks and answer the questions on
the worksheet entitled Asexual vs. Sexual
Reproduction Practice.