Animal Reproduction
Reproduction in Animals
Asexual Reproduction:
– A single living organism that can
produce one or more identical
individuals
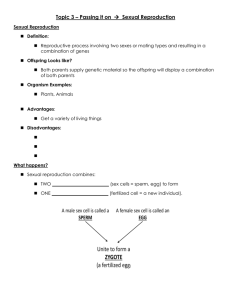
Sexual Reproduction:
– The combination of male and female
gametes, each of which contain half of
the genetic material necessary to the
future offspring.
Gamete: The male or female
reproductive cell that can unite with
another, similar cell from the
opposite sex, through a process
called fertilization
Sperm: The male reproductive cell,
which includes a “tail” for movement
(the whole structure is called a
spermatozoa)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6rauO_M9tb4
Ovum: The female reproductive cell,
the plural is “ova”. Commonly called
an egg.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2-VKgdhfNpY&feature=related
Steps of Vertebrate Reproduction
1. Male gamete fuses with a female
gamete
2. Fusion produces a cell called a
zygote that contains complete
genetic material
3. The zygote divides and transforms
into an embryo with many cells
4. The embryo develops into a small
animal
5. When the animal becomes an adult
it will produce gametes and
reproduce
Conditions for Sexual Reproduction
1. Male and female gametes must be
at the same place at the same time
2. The zygote must obtain the
nutrients and protection it needs to
survive including warmth and
moisture
Oviparous: Lays eggs- reptiles,
birds, amphibians, insects and fish
Viviparous: Fertilized ovum develops
completly inside the mother’s bodyalmost all mammals
Ovoviparous: Produce eggs but do
not lay them, instead keep them
inside their body- snakes