assignment 5 - Science 9 Portfolio
advertisement

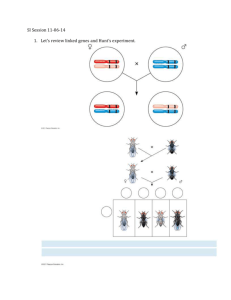
toTopic 5 Assignment DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid Vocabulary: DNA- the set of non-genetic traits, qualities, or features that characterize a person or thing Chromosomes- any of several threadlike bodies, consisting of chromatin, that carry the genes in a linear order: the human species has 23 pairs, designated 1 to 22 in order of decreasing size and X and Y for the female and male sex chromosomes respectively. Adenine- one of the fundamental components of nucleic acids, as DNA, in which it forms a base pair with thymine, and RNA, in which it pairs with uracil. Guanine- a fundamental constituent of DNA and RNA, in which it forms base pairs with cytosine. Cytosine- that is one of the fundamental components of DNA and RNA, in which it forms a base pair with guanine. Thymine- one of the principal components of DNA, in which it is paired with adenine. Gene- the basic physical unit of heredity; a linear sequence of nucleotides along a segment of DNA that provides the coded instructions for synthesis of RNA, which, when translated into protein, leads to the expression of hereditary character. Allele- any of several forms of a gene, usually arising through mutation, that are responsible for hereditary variation. Somatic Cells- one of the cells that take part in the formation of the body, becoming differentiated into the various tissues, organs, etc. Mitosis- the usual method of cell division, characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form, which condenses into chromosomes, each of which separates longitudinally into two parts, one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. Meiosis- part of the process of gamete formation, consisting of chromosome conjugation and two cell divisions, in the course of which the diploid chromosome number becomes reduced to the haploid. Compare mitosis. Genetic Engineering Biotechnology- the use of living organisms or other biological systems in the manufacture of drugs or other products or for environmental management, as in waste recycling: includes the use of bioreactors in manufacturing, microorganisms to degrade oil slicks or organic waste, genetically engineered bacteria to produce human hormones, and monoclonal antibodies to identify antigens. Transgenic- of, pertaining to, or containing a gene or genes transferred from another species Dominant Trait- a trait that will appear in the offspring if one of the parents contributes it. Recessive Trait- a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring. Incomplete Dominance- the appearance in a heterozygote of a trait that is intermediate between either of the trait's homozygous phenotypes. 1. Outline how DNA was discovered. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered it 2. Draw and label the chemical structure of DNA that was modeled by James Watson and Francis Crick. Double Helix 3. What is the genetic code? A genetic code is the specific sequence of genes aligned in different chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell. 4. What enables DNA to have so many variations with only 4 chemicals? There are so many different combinations. 5. Different human cells (somatic cells) have different life spans – fill in the Table. Somatic Cells Life Span Brain cells 30-50 years Red blood cells 120 days Stomach lining cells 2 days Liver cells 200 days Intestine lining cells 3 days Skin cells 20 days 6. Explain the detailed process this illustration demonstrates A sperm and egg go together to make an embryo, which turns into a fetus and becomes a baby. 7. Some organisms can reproduce sexually and asexually. Explain the Advantages and disadvantages of each process. Reproduction Advantages Disadvantages Sexual More variation in genes It takes a lot of energy Asexual You can reproduce faster Doesn’t have any variation 8. Explain how biotechnology can increase or decrease variation. Scientists can change the specific genes in the organisms 9. Describe a positive effect of biotechnology. You can make foods better and plants with fatter foods 10. Describe a negative consequence of biotechnology. We don’t know what it will do to the environment.