SI Session 11-06-14 Let`s review linked genes and Hunt`s
advertisement

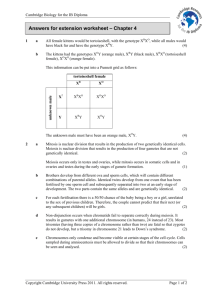
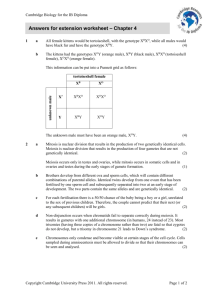
SI Session 11-06-14 1. Let’s review linked genes and Hunt’s experiment. Genes on same chromosome that tend to be inherited together are called linked genes. Hunt knew that the body color gene and the wing length gene were linked. So the f2 generation should only look like the parents if they are linked! But these offspring with nonparental phenotypes are called recombinant types. Because of these recombinant phenotypes, he proposed that some process must occasionally break the physical connection between genes on the same chromosome. This is crossing over. 391 recombinants out of 2300 total offspring. This is 17% of the offspring. This percentage can be represented in a linkage map. The difference between the wings and the black body are about 17 map units. 2. Assuming the aristae length is at map unit 5 and body color is at map unit 48.5, what is the percentage of recombinant phenotypic offspring? (assume that a heterozygous wild-type fly with short aristae and black body is test-crossed with a homozygous mutant fly) 43.5% 3. this figure shows non-disjunction occurring at Meiosis I and at Meiosis II. Memorize the outcomes. ** 4. What is deletion? Duplication? Inversion? Translocation? Deletion removes a chromosomal segment, duplication repeats a segment, inversion reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome, translocation moves a segment from from one chromosome to another. 5. What is Down Syndrome? 6. What is Klinefelter’s Syndrome? Extra x chromosome in males. XXY. sterile 7. What is Turner Syndrome? Monosomy X; x0; sterile 8. What results from a specific deletion in chromosome 5? Cri du chat (cry of the chat) 9. What is chronic myelogenous leukemia caused by? Translocations of chromosomes 10. What is genomic imprinting? Variation in the phenotype dependent upon whether the allele is inherited from the male or female parent is called “genomic imprinting”. For example, Igf2 allele to make mice dwarf are only expressed if allele is from dad. 11. Where do we get our organelle (mitochondria) genes? We get our mitochondria from our mothers since the zygote’s cytoplasm comes from the egg. Sperm doesn’t contribute anything except its nucleus. 12. So we can say that Mendel concluded there were heritable factors, Thomas Hunt Morgan concluded there were genes located on chromosomes. So what makes up this genetic material? 13. Describe Frederick Griffith’s experiment and what his conclusion was. S cells (smooth with a capsule) are virulent. R cells (rough without a capsule) are avirulent. Heat-killed s cells will not kill the mouse but the mixture of heat killed s cells and living r cells will make the mouse die. He called this transformation. 14. Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod announced it was DNA using an experiment using enzymes, but no one believed it, hence Hershey and Chase. Describe Hershey and Chase’s experiment. They cultured bacteriophages in two mediums: One with radioactive sulfur and one with radioactive phosphorus. This tagged the viruses proteins and DNA respectively. Bacteria were introduced in the medium and the bacteriophages attached them and shot in DNA. Infected bacteria after centrifugation went to the bottom on the test tube. The phosphorus one was labeled whereas the sulfur one was labeled in the liquid bc of the phage proteins. 15. Tell me Chargaff’s Rules. 16. Who did a x-ray crystallography of DNA? Who stole this picture and came up with the structure of DNA? 17. DNA replication. 18.