Chapter 12 Review (Exam 3)
advertisement

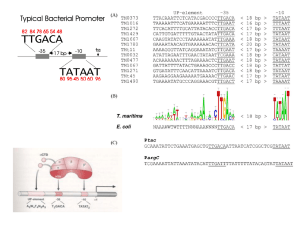
Chapter 12 Questions: 1. What is the main goal of transcription? What is the difference between the product of transcription produced by prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 2. In a given cell, are all genes being expressed at the same time? Please explain your answer. 3. Please list the appropriate enzymes (both prokaryotic and eukaryotic) that catalyze the process of transcription for each question below. a. All the enzymes found in nature that can transcribe RNAs b. All enzymes that transcribe rRNAs c. All enzymes that transcribe mRNA d. All enzymes that transcribe protein coding genes e. All enzymes that snRNAs (splicing RNAs) f. All enzymes that do not transcribe protein coding genes 4. Please draw a cartoon of the eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. On your diagram, please note the active site as well point out the site(s) that are important for release from the promoter region and name it. Please state which molecules will be found in the active site and explain why they can be found there. 5. Please briefly explain how nucleotides are held within the active site of RNA polymerase II during transcription. 6. Why do nucleotides need to be held within the active site of RNA polymerase II? 7. Please explain how RNA polymerases from different species are conserved. Why do think RNA polymerases are conserved? 8. Which of the two enzymes listed below is more error prone? Please explain your answer. a. DNA polymerase b. RNA polymerase II 9. Please draw a picture of a promoter. Please note which sequences within the promoter are part of the core promoter and which sequences are regulatory sequences. 10. Please state three types of factors that bind the promoter. Please state where they bind within the promoter. 11. Please state all types of regulatory elements that act to promote efficient transcription. Which one(s) work over long distances? Which types of regulatory transcription factors might bind these? 12. Please state all types of regulatory elements that act to repress transcription. Which one(s) work over long distances? Which types of regulatory transcription factors might bind these? 13. Please state all roles for general transcription factors. Please state which general transcription factor(s) are involved in each process. 14. Please describe how the transcription pre-initiation complex is formed. 15. Why does the DNA need to be melted for transcription to occur? Which protein(s) are involved in the process? 16. Which core promoter sequence is ultimately responsible for allowing the formation of the pre-initiation complex? Please explain your answer. 17. Why is it important for the RNA polymerase II to escape the core promoter? Please explain how this occurs. 18. From the point where the RNA polymerase II escapes the core promoter, please list the proteins that interact with the pol II CTD and state the function of each. 19. Which amino acid sequence within the RNA polymerase Pol II CTD is the most important. Please explain what happens to this sequence during promoter binding and promoter escape. 20. Does eukaryotic transcription produce an mRNA. If not, please state which RNA is produced. Which process(es) must occur to allow for maturation of the RNA? Please discuss in detail whether these process(es) occur concurrent with transcription. 21. Are there any proteins that have the ability to impede RNA polymerase II progression during transcription? If so, please state which types of proteins are capable of impeding RNA polymerase II progression. 22. Please discuss the role of FACT during transcription. How does FACT work? 23. Pls. name the appropriate regulatory transcription factor for the phrase below. a. Causes an increase of transcription from your gene of interest. b. Causes a decrease of transcription from your gene of interest. c. A mutation in the promoter sequence that interrupts binding of this transcription factor results in higher than expected transcription (mRNA produced). d. A mutation in the promoter sequence that interrupts binding of this transcription factor results in lower than expected transcription (mRNA produced).