Lesson_6 Periodic Trends Graphing Assignment
advertisement

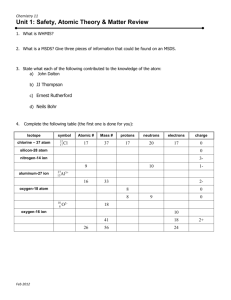
SCH 3U Trends in the Periodic Table: Graphing Assignment Introduction: In this assignment you will construct three different graphs to obtain a visual representation of the changes in three properties of elements as their atomic number increases. By completing this activity, you should see that elements are grouped on the periodic table according to similarities in these properties. The three properties you will investigate are: Atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Materials: Data for first 20 elements (below) 3 sheets of graph paper Procedure: 1) Turn the graph paper sideways so that the long side becomes the x-axis. The x-axis will represent the atomic number for all three graphs. Spread out values so they fill the length of the x-axis. 2) Label the y-axis with the given property and establish a scale that begins with ‘0’. 3) Graph the data provided. 4) Label each point with the corresponding element symbol. 5) Between elements 2 and 3, 10 and 11, 18 and 19, draw a red vertical line to separate the four PERIODS of elements. Label the sections 1 – 4. 6) In each section (1 – 4), draw a curve of best fit among the points (Don’t play connect the dots!) 7) Be sure all axes are labeled (title and units) and each graph has a descriptive title. Data: See page 2 Follow-Up Questions: Please answer with complete sentences Atomic radius 1) According to the graph, what happens to the radius (size) of an atom as you move across a period (row) of the periodic table? 2) According to the graph, what happens to the radius (size) of an atom as you move down a group (column) of the periodic table? Ionization Energy 1) Generally, what happens to the ionization energy of an atom as you move across a period of the periodic table? 2) Generally, what happens to the ionization energy of an atom as you move down a column of the periodic table? 3) How do these trends differ from atomic radius? Electronegativity 1) Generally, what happens to the electronegativity of an atom as you move across a period? 2) Generally, what happens to the electronegativity of an atom as you move down a column? 3) How are these trends differ from atomic radius? Trends in the Periodic Table: Graphing Assignment Data Tables: Table 1: Atomic Number and Atomic Radius for elements 1 – 20 Atomic Number Atomic Radius (pm) Atomic Number 1 37 11 2 32 12 3 152 13 4 111 14 5 79 15 6 77 16 7 74 17 8 76 18 9 71 19 10 69 20 Atomic Radius (pm) 186 160 143 117 110 102 100 97 227 197 Table 2: Atomic Number and Ionization Energy for elements 1 – 20 Atomic Number Ionization Energy (kJ) Atomic Number 1 1294 11 2 2336 12 3 511 13 4 886 14 5 787 15 6 1071 16 7 1380 17 8 1294 18 9 1656 19 10 2048 20 Ionization Energy (kJ) 486 725 569 775 1046 985 1236 1496 408 581 Table 3: Atomic Number and Electronegativity for elements 1 - 20 Atomic Number Electronegativity Atomic Number 1 2.1 11 2 No Value 12 3 1.0 13 4 1.5 14 5 2.0 15 6 2.5 16 7 3.0 17 8 3.5 18 9 4.0 19 10 No Value 20 Electronegativity 0.9 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.5 3.0 No Value 0.8 1.0