Honors Biology semester review
advertisement
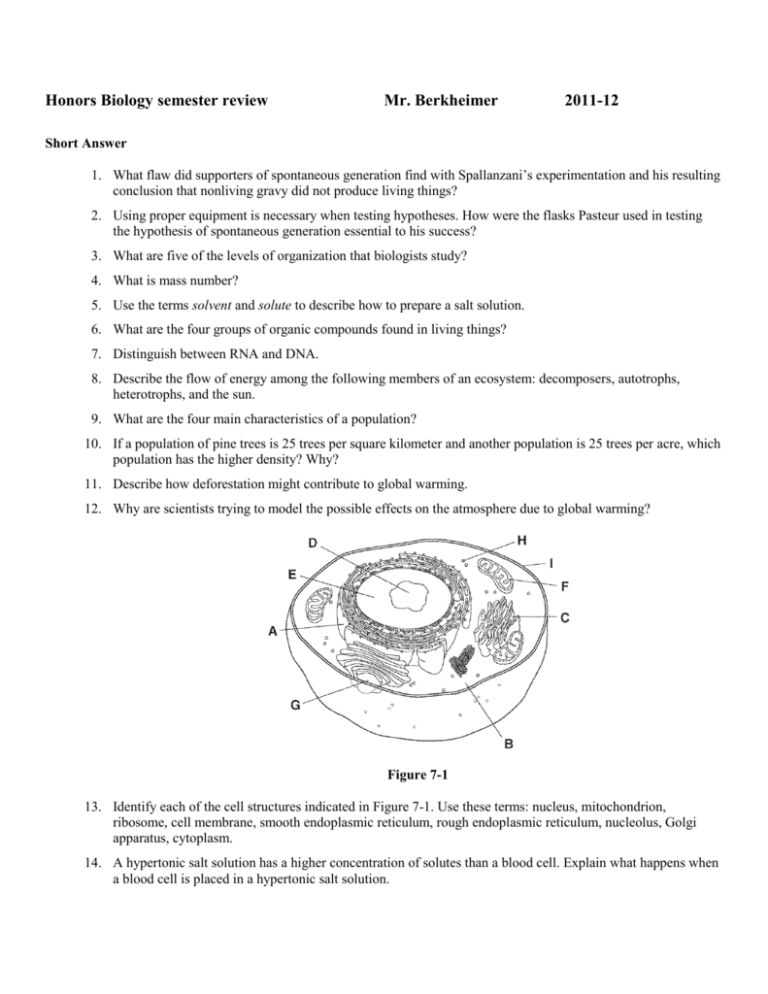
Honors Biology semester review Mr. Berkheimer 2011-12 Short Answer 1. What flaw did supporters of spontaneous generation find with Spallanzani’s experimentation and his resulting conclusion that nonliving gravy did not produce living things? 2. Using proper equipment is necessary when testing hypotheses. How were the flasks Pasteur used in testing the hypothesis of spontaneous generation essential to his success? 3. What are five of the levels of organization that biologists study? 4. What is mass number? 5. Use the terms solvent and solute to describe how to prepare a salt solution. 6. What are the four groups of organic compounds found in living things? 7. Distinguish between RNA and DNA. 8. Describe the flow of energy among the following members of an ecosystem: decomposers, autotrophs, heterotrophs, and the sun. 9. What are the four main characteristics of a population? 10. If a population of pine trees is 25 trees per square kilometer and another population is 25 trees per acre, which population has the higher density? Why? 11. Describe how deforestation might contribute to global warming. 12. Why are scientists trying to model the possible effects on the atmosphere due to global warming? Figure 7-1 13. Identify each of the cell structures indicated in Figure 7-1. Use these terms: nucleus, mitochondrion, ribosome, cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus, cytoplasm. 14. A hypertonic salt solution has a higher concentration of solutes than a blood cell. Explain what happens when a blood cell is placed in a hypertonic salt solution. 15. What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotroph? Give an example of each type of organism. 16. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis in both symbols and words. Figure 8-3 17. Identify the structure shown in Figure 8-3 and describe its function. 18. Compare photosystems I and II. 19. List the three main stages of cellular respiration in order. Where does each stage take place in the cell? 20. Describe glycolysis in terms of energy input, energy output, and net gain of ATP. 21. Why is the Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle? 22. How do cancer cells differ from normal cells? Essay 23. How would you determine whether something is living or nonliving? 24. A biologist is doing research on a pack of wolves living in a particular section of a forest in northern Minnesota. What levels of organization could this biologist be studying? 25. Under what conditions would you use a compound light microscope and each type of electron microscope? 26. Compare and contrast two common laboratory techniques: cell culturing and cell fractionation. 27. Compare protons, electrons, and neutrons with respect to location within atoms, electric charge, and mass. 28. What relationship exists between the mass number of an element and the isotopes of that element? 29. Explain the difference between ionic compounds and covalently bonded compounds. 30. Compare and contrast adhesion and cohesion, using capillary action as an example. 31. How can you account for the great number, size, and complexity of organic compounds? 32. Compare enzyme activity to a lock and key. 33. How does a food web differ from a food chain? 34. Describe the three types of ecological pyramids. 35. Describe the roles of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. 36. Describe the biological significance of the carbon cycle. Where is carbon found in the biosphere? 37. Describe the greenhouse effect and explain how it maintains Earth’s temperature range. 38. Name and define the three main classes of symbiotic relationships. Give examples of each. 39. Describe the stages of primary succession in land environments, including lichens, mosses, grasses, shrubs, and trees. 40. Discuss four ways population sizes can change. 41. Differentiate between exponential and logistic growth. 42. Explain the limiting factors that control population growth. 43. Explain how predator and prey populations limit each other’s growth rates. 44. Differentiate between density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors. 45. Compare some ecologists’ view of world population growth with that of some economists. 46. Discuss biodiversity as a source of medicines. Give an example. 47. What are introduced species? How are they a threat to biodiversity? 48. Discuss the health effects of damage to the ozone layer and the steps being taken to help deal with the problem. 49. Summarize three statements from the cell theory. Explain the significance of the cell theory to biology. 50. Compare prokaryotes with eukaryotes. Give an example of each type of cell. 51. Distinguish between microtubules and microfilaments. Describe two functions for each kind of structure. 52. Compare the cell membrane to a mosaic. 53. Describe what happens when sugar solutions with two different concentrations are placed on opposite sides of a semipermeable membrane in a container. 54. How do facilitated diffusion and active transport differ? 55. Discuss the levels of organization in multicellular organisms and explain why these levels are not used to describe unicellular organisms. 56. Discuss the relationship between autotrophs and heterotrophs. Do heterotrophs depend on autotrophs for their survival? Explain your answer. 57. Compare the storage capacity of ATP and glucose. How does the cell use each of these molecules to store energy? 58. Describe the experiments of van Helmont, Priestley, and Ingenhousz. How did the work of these scientists contribute to our current understanding of photosynthesis? 59. Trace the events that occur in the thylakoid membrane during the light-dependent reactions. 60. What happens to the electrons in a chlorophyll molecule when light shines on it? Does the chlorophyll molecule ever run out of electrons? Explain your answer. 61. Identify three factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis and explain the effect of each. 62. List the main events of glycolysis. How many ATP molecules are produced and consumed by glycolysis? What effect does the presence of oxygen have on the events that follow glycolysis? 63. Compare lactic acid fermentation with alcoholic fermentation. Where does each process occur? What are the products of each process? 64. Describe the main steps and the results of one turn of the Krebs cycle. 65. What happens to muscle cells during intense physical activity? 66. Compare photosynthesis with cellular respiration. 67. Relate ratio of surface area to volume to cell growth and cell division. 68. What kinds of problems does growth cause for cells? How does cell division help a cell solve these problems? 69. List and describe the main events of the cell cycle. Illustrate your description with a diagram of the cell cycle. 70. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Other USING SCIENCE SKILLS Common Metric Units Length Mass 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm) 1 meter = 1000 millimeters (mm) 1000 meters = 1 kilometer (km) 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g) 1 gram = 1000 milligrams (mg) 1000 kilograms = 1 metric ton (t) Volume Temperature 1 liter (L) = 1000 milliliters (mL) 1 liter = 1000 cubic centimeters (cm3) 0ºC = freezing point of water 100ºC = boiling point of water Figure 1-3 71. Using Tables and Graphs What four common metric units in Figure 1-3 are used to measure length? 72. Applying Concepts Referring to Figure 1-3, why are conversions easier to do using the metric system rather than using traditional English units, such as inches, feet, and yards? 73. Using Tables and Graphs What is the boiling point of water in degrees Celsius? 74. Applying Concepts Using Figure 1-3, what number does the prefix kilo- represent? 75. Calculating If you have 2 L of water, how many milliliters do you have? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Element Symbol Protons Neutrons Electrons Atomic Number Mass Number Hydrogen H 1 1 Helium He 2 Carbon C 6 Oxygen O 8 Neon Ne Aluminum Al Zinc Zn 4 6 8 10 10 13 20 27 30 30 65 Figure 2-1 76. Calculating Based on Figure 2-1, what is the mass number of carbon? 77. Applying Concepts Based on Figure 2-1, what is the atomic number of oxygen? 78. Applying Concepts Using Figure 2-1, how many electrons does an atom of aluminum contain? 79. Applying Concepts According to Figure 2-1, an atom of which element contains two neutrons? 80. Applying Concepts Based on Figure 2-1, which element has a mass number of 16? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 3-5 81. Applying Concepts What three scientific approaches do ecologists use to explain complex relationships, such as in the energy pyramid in Figure 3-5? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 8-6 82. Interpreting Graphics What process is shown in Figure 8-6? 83. Interpreting Graphics What structure is shown in Figure 8-6? 84. Interpreting Graphics Look at Figure 8-6. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions? 85. Interpreting Graphics What are the products of the Calvin cycle shown in Figure 8-6? 86. Interpreting Graphics In Figure 8-6, what chemical is converted to sugar? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 9-3 87. Interpreting Graphics What process does Figure 9-3 show? 88. Interpreting Graphics Look at Figure 9-3. Where do the electrons moving along the inner membrane come from? 89. Interpreting Graphics Where do the electrons moving along the inner membrane in Figure 9-3 end up? 90. Inferring Look at the arrows and H+ ions in Figure 9-3. Which direction do most of the H+ ions move in? What is the result of this movement? 91. Interpreting Graphics ATP synthase is an enzyme. Find ATP synthase in Figure 9-3. What reaction does ATP synthase catalyze when an H+ ion passes through its channel? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 10-4 92. Interpreting Graphics What does Figure 10-4 represent? How do you know if this is an animal cell or a plant cell? 93. Inferring What is the chromosome number of the cell shown in Figure 10-4? 94. Inferring Identify the structures labeled X and Y in Figure 10-4. 95. Applying Concepts List the correct order for the diagrams in Figure 10-4. 96. Predicting After the steps shown in Figure 10-4 are arranged in the correct order, what would a diagram of the next step show?








