CH 250 Block 3 2012 Exam #3 (100 points) Name: Date: Honor
advertisement

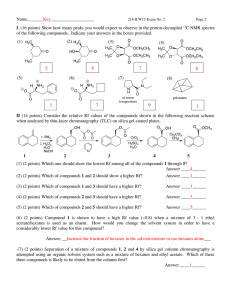
CH 250 Block 3 2012 Exam #3 (100 points) Name: Date: Honor Code: “It is not that I'm so smart. But I stay with the questions much longer.” ― Albert Einstein The Rules: You have 3 hours to complete the exam unless you have provided me with documentation for extra time. When you are done with your exam, please place it in the box outside my office. In fairness to all, anyone who turns in an exam late will receive a grade of zero! You may use your model kits. A periodic table, pKa table, IR table, and 1H NMR table are provided as a supplementary packet. No notes or textbook allowed. This exam is an individual assessment—no teamwork, paid consultants, etc. Please turn off all electronic devices and keep them safely stowed throughout the exam. You may not use electronic devices of any kind for any reason during the exam. You may take the exam in Olin 1 or the Olin fishbowl. Be sure to read the instructions for each question. It may be helpful to skim the entire exam and solve the easier questions first. 1 1) (10 points) The following compounds may undergo autooxidation in the presence of oxygen and light to form peroxide compounds (e.g. R-O-O-H). a) Rank the following compounds (1 = most reactive, 3= least reactive) toward autooxidation. Explain your reasoning. b) What is the most likely rate-determining step in the autooxidative radical chain reaction of the compounds above? How does this relate to your answer for part a? c) Explain how BHT (drawn below) functions as a “stabilizer” when present in low concentrations in ether solvents and food products. 2 2) (14 points) a) Draw the expected product(s) of the following reactions; show relative stereochemistry on products, where relevant: b) Draw a detailed mechanism for the top reaction above (i.e. 1) Br2, H2O; 2) NaOH) 3 3) (16 points) CHOOSE TWO out of the THREE following syntheses (a-c) and propose a plausible synthetic route. Show all reagents required and key intermediates produced. a) b) c) 4 4) (24 points) Pick your favorite reactions! (Are we having fun yet?) Choose your favorite method for completing the following functional group transformations. Indicate the reagents required, and draw the product formed, indicating any relevant stereochemistry. a) Oxidize the alcohol below: b) Convert the alcohol to an alkyl bromide: c) Reduce the ketone to an alcohol. d) Convert the alkene to a syn-diol: e) Convert the alkene to an anti-diol: 5 f) Reduce to an alkene: g) Convert 2-methyl-2-pentene to 2-methyl-2-pentanol (draw starting material, reagents, and product) h) Convert 2-methyl-2-pentene to 2-methyl-3-pentanol (draw starting material, reagents, and product) 5) (6 points) Draw a detailed mechanism for your reaction from question 4c. Be sure to indicate all bondforming and bond breaking steps. 6 6) (18 points) An ether with chemical formula C6H14O produces the following 1H and 13C NMR spectra. a) Predict the structure of this compound correlate and indicate which atoms in your molecule produce each signal. (Note: In the 1H NMR, the signal at ~1.1 ppm is a doublet, and the signal at ~3.7 ppm is a multiplet. In the 13C spectrum, the signal at ~77 ppm in is CDCl3) 7 b) Propose a synthesis the compound from part a using any organic starting materials containing no more than 3 carbons and any other reagents you need. 8 7) ( 12 points) A novice chemist has tried to achieve a synthesis of Compound B from Compound A using the route shown below. List any mistakes this chemist has made and modify the route and/or reagents as necessary (You must still begin with compound A and produce compound B.) “How did it get so late so soon?” -- Dr. Seuss 9 10