How the Sodium Potassium Pump Works. The sodium
advertisement

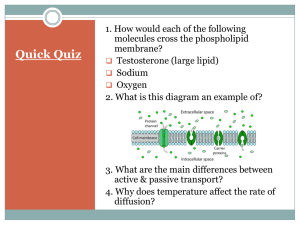
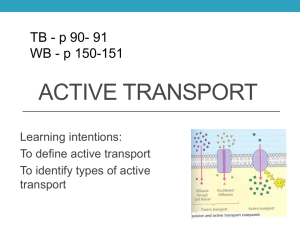
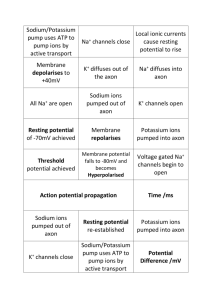
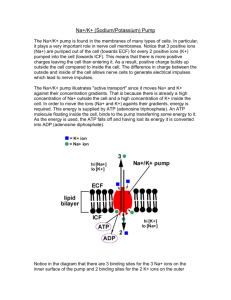
How the Sodium Potassium Pump Works. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of an active transport system. It pumps ions across the plasma membrane from areas of low to high concentration. It is present is essentially all cells and is found in greater numbers in the plasma membrane of nerve cells. It results in a positive charge on the outside of the cell. This aids in the movement of electrical impulses between nerve cells. Use animation #1 to answer the following questions. 1. What molecule provides energy for the sodium-potassium pump? 2. Do you remember what is released when a phosphate is removed from ATP? 3. What do you think Na+ represents? 4. What do you think K- represents? 5. Where is the sodium level greater? (inside the cell or outside the cell) 6. Where is the potassium level greater? (inside the cell or outside the cell) 7. What does it mean by “each ion is moving against its concentration gradient”? 8. The movement of the sodium-potassium pump can only be achieved by the constant expenditure of what? 9. Why does the sodium-potassium pump require energy from ATP? Scroll down and complete the review questions. What did you score? _________ correct out of 5