Study Guide Aristotle: Used a classification system which had only
advertisement

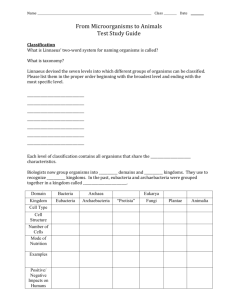
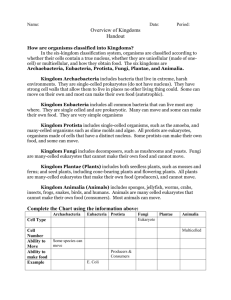
Study Guide Aristotle: Used a classification system which had only two groups: plants or animals Linnaeus: Known as the father of taxonomy Developed a seven-level system of classification Used binomial nomenclature which is a two-part name for an organisms which is the scientific name (composed of the genus and species). Robert Hooke: In 1665, he was the first person to describe cells when looking at cork with a microscope. Hooke observed cells in plants and fungi. Anton von Leeuwenhoek: discovered single-celled organisms (protists) in pond scum in 1673. first to see blood cells, bacterial cells, and yeast cells. Matthias Schleiden: concluded that all plant parts were made of cells in 1838. Theodor Schwann: concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells in 1839. Rudolf Virchow: stated that all cells could form only from other cells in 1858. Common Characteristics That All Living Things Share: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Grow and Develop Have genetic material Use energy Reproduce Respond to their environment Have one or more cells Levels of Classification 1. Domain 2. Kingdom 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Domains 1. Archaea 2. Bacteria 3. Eukarya Six Kingdoms 1. Archaebacteria 2. Eubacteria 3. Fungi 4. Protista 5. Animalia 6. Plantae Types of Cells 1. Cells with no nucleus are prokaryotic. Archaebacteria Eubacteria 2. Cells that have a nucleus are eukaryotic Fungi Protista Animalia Plantae State the parts of the cell theory. 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. 4. Surface area Explain why cells are so small. Most cells are small because food and waste must pass through the cell surface. As a cell’s volume increases, its surface area grows. But volume increases faster than the surface area. The area of a cell’s surface–compared with the cell’s volume–limits the cell’s size. The ratio of the cell’s outer surface to the cell’s volume is called the surface area-to-volume ratio: Surface area to volume ratio = surface area Volume Describe how eubacteria are different from archaebacteria Archaebacteria. • Are similar to bacteria in some ways and are similar to eukaryotic cells in other ways. • Three types of archaebacteria are heat-loving, salt-loving, and methane-making. Heat-loving and salt-loving archaebacteria live in extreme conditions and are sometimes called extremophiles. Eubacteria • Are also called bacteria and are the world’s smallest cells. They do not have membrane covered organelles, but they do have tiny, round organelles called ribosomes. • Some bacteria live in soil and water. Others live in, or on, other organisms. Parts of a Typical Prokaryotic Cells 1. 2. 3. 4. Circular DNA, cell membrane, and cell wall flagellum Prokaryotic Cell below: Describe the parts of a cell. • Levels of Body Organization Cells-Tissues-Organs-Organ Systems- Organisms Example below: Please be able to identify the parts of a plant cell and animal cell. See the cells below: