Overview of Kingdoms Handout
advertisement

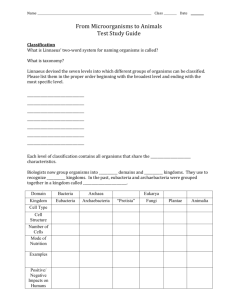
Name: Date: Period: Overview of Kingdoms Handout How are organisms classified into Kingdoms? In the six-kingdom classification system, organisms are classified according to whether their cells contain a true nucleus, whether they are unicellular (made of onecell) or multicellular, and how they obtain food. The six kingdoms are Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Kingdom Archaebacteria includes bacteria that live in extreme, harsh environments. They are single-celled prokaryotes (do not have nucleus). They have strong cell walls that allow them to live in places no other living thing could. Some can move on their own and most can make their own food (autotrophic). Kingdom Eubacteria includes all common bacteria that can live most any where. They are single celled and are prokaryotic. Many can move and some can make their own food. They are very simple organisms Kingdom Protista includes single-celled organisms, such as the amoeba, and many-celled organisms such as slime molds and algae. All protists are eukaryotes, organisms made of cells that have a distinct nucleus. Some protists can make their own food, and some can move. Kingdom Fungi includes decomposers, such as mushrooms and yeasts. Fungi are many-celled eukaryotes that cannot make their own food and cannot move. Kingdom Plantae (Plants) includes both seedless plants, such as mosses and ferns; and seed plants, including cone-bearing plants and flowering plants. All plants are many-celled eukaryotes that make their own food (producers), and cannot move. Kingdom Animalia (Animals) includes sponges, jellyfish, worms, crabs, insects, frogs, snakes, birds, and humans. Animals are many celled eukaryotes that cannot make their own food (consumers). Most animals can move. Complete the Chart using the information above: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Cell Type Cell Number Ability to Move Ability to make food Example Fungi Eukaryote Plantae Animalia Multicelled Some species can move Producers & Consumers E. Coli The Six Kingdoms: Summary Chart Archaebacteria Simple, unicellular organisms with no true nucleus and live in extreme places Simple, unicellular organisms with no true nucleus that live almost everywhere Eubacteria Simple, unicellular, or mulitcellular organisms. They have a true nucleus Protista Unicellular or multicellular organisms, fungi obtain food from dead organisms Fungi Muticellular organisms; plants use cholorphyll to make their own food. Plantae Multicellular organisms; animals get their food by eating other organisms. Animalia List Characteristics for each Kingdom I. Archaebacteria 1. 2. 3. II. Eubacteria 1. 2. 3. 4. III. Protista (Protists) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. IV. Fungi (Fungus) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. V. Plantae (Plants) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. VI. Animalia (Animals) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.