36 - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

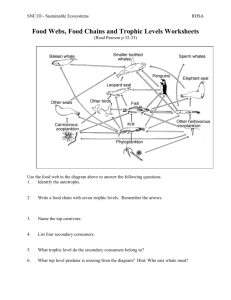
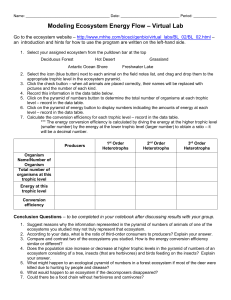
Concept Check Questions 36.1 1. How are the movement of energy and the movement of chemicals different? 2. In the following food chain, identify the trophic levels: An owl eats a mouse that ate berries. 3. Draw a food chain with at least three trophic levels. 36.2 1. What does primary productivity measure? What does it tell you about an ecosystem? 2. What point does each type of ecological pyramid emphasize? 3. What does the shape of the energy pyramid indicate? 36.3 1. Identify three basic steps of chemical cycling. 2. Explain how photosynthesis and respiration are involved in cycling carbon and oxygen. 3. Describe three roles that bacteria play in the nitrogen cycle. 4. Follow a raindrop through one possible path through the water cycle, ending as water vapor in the atmosphere. 36.4 1. Describe how increased quantities of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere may contribute to global warming. 2. Give an example showing how pollution relates to biological magnification. 3. How can deforestation impact the carbon and water cycles? 4. What is the relationship between chlorofluorocarbons and ozone? 36.5 1. Describe two arguments for preserving biodiversity. 2. What are four main threats to biodiversity? 3. Describe how zoned reserves may help conservation efforts? Answers Concept Check Questions 36.1 1. How are the movement of energy and the movement of chemicals different? - Energy flows through an ecosystem. Chemicals are recycled. 2. In the following food chain, identify the trophic levels: An owl eats a mouse that ate berries. - Plant=producer, mouse=primary consumer, owl=secondary consumer 3. Draw a food chain with at least three trophic levels. -Plant as a producer herbivore or omnivore as primary consumer carnivore or omnivore as secondary consumer 36.2 1. What does primary productivity measure? What does it tell you about an ecosystem? - The rate at which living, organic material is made. The maximum amount of energy in an ecosystem 2. What point does each type of ecological pyramid emphasize? -Energy: loss of energy each trophic level. Biomass- amount of living material (stuff) in each trophic level. Numbers: actual number of living things in each trophic level 3. What does the shape of the energy pyramid indicate? -Amount of energy available at each level, higher in the pyramid has less energy available to them. 36.3 1. Identify three basic steps of chemical cycling. - Producers convert inorganic organics; consumers feed on producers; decomposers break down producers and consumers into inorganics 2. Explain how photosynthesis and respiration are involved in cycling carbon and oxygen. - Photosyn: producers take in CO2 to make organic products (sugar); consumers release CO2 as a waste product 3. Describe three roles that bacteria play in the nitrogen cycle. -Fixation- nitrogen gas to ammonia, nitrification- ammonium to nitrates; denitrification- nitrates into nitrogen gas 4. Follow a raindrop through one possible path through the water cycle, ending as water vapor in the atmosphere. Precipitation runoff groundwater evaporation / transpiration condensation 36.4 1. Describe how increased quantities of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere may contribute to global warming. - Allows sun light to reach earth surface, but keeps heat trapped. More CO2 more heat trapped. 2. Give an example showing how pollution relates to biological magnification. -Pollutant concentrates as go up food chain. So producer and primary consumer have less concentration of pollution than a secondary or tertiary consumer. Quarternary would have the highest concentration. 3. How can deforestation impact the carbon and water cycles? - Less producers to absorb carbon dioxide, transpiration affected changing precipitation patterns 4. What is the relationship between chlorofluorocarbons and ozone? - Chlorine in CFC break down O3 (ozone) into O2 (oxygen) 36.5 1. Describe two arguments for preserving biodiversity. -Beauty, interconnectedness of species, sources for basic needs, medicines 2. What are four main threats to biodiversity? -pollution, habitat destruction, introduced species, and overexploitation 3. Describe how zoned reserves may help conservation efforts? -Zoned reserves are undisturbed areas by humans usually surrounded by buffer zones with minimal areas of disturbance. Used to balance human needs and habitat preservation.