Test 1 Review - Principals of Ecology
advertisement

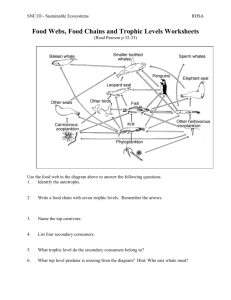
Principles of Ecology Test Date: ______________________________ 1. Define biotic. List at least 5 biotic factors in an ecosystem. 2. Define abiotic. List at least 5 abiotic factors in an ecosystem. 3. Be able to interpret a food chain and food web. Know how to identify trophic levels when examining chains/webs. 4. If the primary producers have 1700 kcal of energy, and they transfer 10.6% of their energy to the next trophic level, which in turns transfers 9.7% of their energy to the next trophic level, how much of the original energy will the third trophic level receive? 5. Be able to interpret an energy pyramid, biomass pyramid, and pyramid of numbers. 6. There are 45,000 plants living in a community. These plants support 3,300 mice. The mice provide food for the 87 snakes that live in the area, which are consumed by the 6 hawks in the area. Create a pyramid of numbers for this scenario. 7. Define herbivore. In which trophic level would you find herbivores? 8. Define omnivore. In which trophic level(s) would you find omnivores? 9. Define carnivore. 10. List the five ecological levels of organization in order from smallest to largest. Define each level and give an example of each. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 11. What is a keystone species? 12. Why are decomposers important to an ecosystem? 13. Draw a food chain containing 5 trophic levels. 14. What does an arrow represent in a food chain/web? 15. Define biomass. 16. Define energy pyramid. 17. In which trophic level would you find plants? 18. Differentiate between a generalist and a specialist. Which one is more advantageous for an organism? 19. Why do ecologists measure population size by using quadrats? 20. Which important biological processes are involved in the carbon and oxygen cycles? 21. What do ecologists study? 22. List the trophic levels in order. 23. At which level of organization are abiotic factors considered? 24. Define biodiversity. How does removing a keystone species affect biodiversity of an area? 25. Define detritivore. Give at least 2 examples. 26. Define decomposer. Give at least 2 examples. What important role do decomposers have in the ecosystem? 27. How do food chains and food webs compare? 28. What happens to energy as it moves through a food web/chain? 29. What are the four elements that cycle through the ecosystems, and why are they important? 30. What type of organism plays a key role in the nitrogen cycle? List 4 examples of this type of plant. 31. From where does the phosphorus originate in the phosphorus cycle? 32. Can plants and animals obtain nitrogen directly from the atmosphere? What process must plants use to make the nitrogen available for use? 33. Bacteria convert nitrogen into ammonia by a process called ___________________________________. 34. Of the four cycles discussed in class, which one does not exist as a gas? 35. Why is it critical for organisms to have phosphorus? 36. How are phosphates returned to the environment after being used by plants and animals? 37. Not all carbon flows freely through the carbon cycle. Some carbon is stored for very long periods of time in areas called carbon sinks. Give an example of a carbon sink. Please Note: This review is NOT comprehensive. Simply memorizing this review does not ensure that you will make an A on the test. You are responsible for all material presented and discussed in class.