power point
advertisement

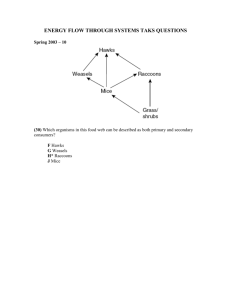
What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment Biosphere air • The combined portions of the planet in which all life exists • Includes land, water and air or atmosphere • Extends from about 8 water km above Earth’s land surface to as far as In which part of the biosphere 11 km below the do you live (air, water, land)? surface of the ocean Levels of organization • • • • • • • Individual Species Population Community Ecosystem Biome Biosphere Are the members of this class a population or a community? Energy flow • Sunlight is the main source of energy for life on Earth • Autotrophs or producers use energy from the environment to make their own food Photosynthesis • Autotrophs (producers) that capture energy from the sun use photosynthesis Chemosynthesis • Autotrophs (producers) that capture chemical energy use chemosynthesis Consumers are heterotrophs • Herbivores • Carnivores Carnivore • Omnivores • Detritivores Decomposers What type of consumer are you? Feeding relationships Energy flows in direction of arrows The grasshopper eats the grass The snake eats the grasshopper Food chain • One way flow of energy from sun (or chemicals) to producer(s) to consumer(s) • List the source of energy, the producer, the primary consumer (herbivore) and the secondary consumer (carnivore) Food web • Complex series of interconnected food chains • List the producers, primary consumer(s), and secondary consumer(s) Marine food web • Energy – sun • Producers – phytoplankton, seaweed • Primary consumers – zooplankton, mussels, limpets • Secondary consumers – prawn, crab, whelk, gull, lobster, mussels • Tertiary consumers – gull, lobster, fish, whelk, crab • Quaternary consumers – gull, lobster Trophic levels • Each step in a food chain or food web • Each consumer depends on the trophic level below it for energy • Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to the organisms in the next trophic level • Three types of pyramids illustrate the ecological relationship between trophic levels (see pages 77 -78) Ecological Pyramids Section 3-2 Energy Pyramid Shows the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level. Organisms use about 10 percent of this energy for life processes. The rest is lost as heat. Biomass Pyramid Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Typically, the greatest biomass is at the base of the pyramid. Go to Section: Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level.