ES 3.4 PPT
advertisement

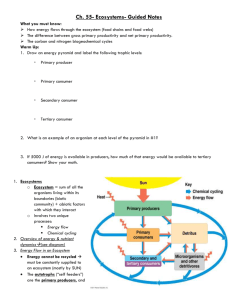
Energy Flow in Ecosystems 3.4 Energy Flow When an animal eats a plant, energy is transferred from plant to animal The same thing happens when an animal eats another animal The transfer of energy through an ecosystem can be traced This helps scientists see how organisms are connected and how much energy is transferred Food Chains Show how organisms in an ecosystem get their food Each organism is a link in the chain and provides food for the next link Always starts with a producer Always ends with a consumer Example: Grasslands of Africa pg. 96 Acacia trees producer As producers, the trees make their own food using sunlight Giraffes primary consumer They eat the leaves and get some of the energy stored in them Lions secondary consumer Lions feed on giraffes and get the energy stored in their cells Food Webs Most organisms are a part of more than one food chain This network of feeding relationships is called a food web Eating many different foods can help a consumer make sure it can find enough food Pg. 97 Trophic Levels Feeding level in a food chain or web Producers make up the first trophic level Green plants in a grassland ecosystem Algae in an ocean ecosystem In few ecosystems, bacteria form the first level Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary The second trophic level is made up of herbivores (primary consumers) The third trophic level is made up of carnivores (secondary consumers) These feed on primary consumers In some food chains, there is a fourth or fifth level of consumers (tertiary consumers) These consumers eat other consumers Energy Pyramids Which are there more of: producers or consumers? _________________ Trophic levels form a pyramid because there are many more producers than primary consumers Producers form the bottom of the pyramid There are more primary consumers than secondary consumers Think about it this way… A field of grass can only support a certain number of rabbits The number of rabbits can only support a smaller number of bobcats The bobcats can only support an even smaller number of cougars Energy Transfer pg. 99 An energy pyramid shows the amount of energy available at each trophic level Each time energy is transferred, about 90% is lost Some is lost to heat and escapes into the atmosphere Only 10% gets stored in the consumer As you move up the pyramid, less food energy is available The pyramid break down The first trophic level is the largest and has the most energy Each level above it has less energy and fewer species The top level (tertiary) has the smallest amount of energy This is why there are more small animals than large animals in an ecosystem Food chains only have 4-5 links Vocabulary Food Chain Food Web Trophic Level Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer