VSEPR Practice Molecules and Ions
advertisement

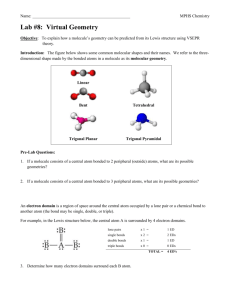
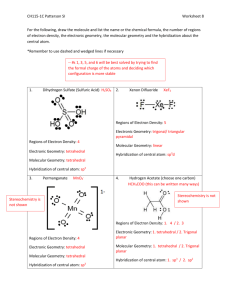
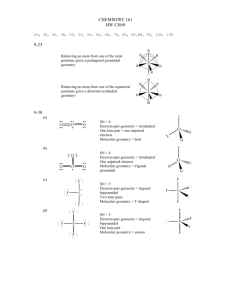
VSEPR Practice Molecules and Ions Here are forty-six molecules and ions that exhibit almost all the possibilities of molecular geometry. They are listed in order of numbers of electron domains - "regions of high electron density" - around the central atom(s). There are several molecules of each basic geometry. For the purposes of VSEPR a multiple bond is counted as a single "domain", a single bond is a "domain", and a lone pair (LP) is a "domain". In some molecules the preferred central atom is underlined if there might be an ambiguity in writing the Lewis structure. In this list only one molecule, C2H2, has two central atoms. The five basic geometries of the electron domains (linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral) are shown in Table 9.1, p. 319, Brown&LeMay. The thirteen possible molecular geometries are shown in Tables 9.2, p. 321, and 9.3, p. 324. 2 domains - domain geometry is linear, 180° bond angle (sp hybridization) molecular geometry is linear Examples are: CO2, HCN, BeCl2, C2H2 3 domains - domain geometry is trigonal planar, 120° bond angles (sp2 hybridization) no LP on central atom so molecular geometry is trigonal planar Examples are: NO3-, SO3, BF3, CO32 one LP on central atom so molecular geometry is bent Examples are: SO2, O3, NO2-, PbCl2 4 domains - domain geometry tetrahedral, 109.5° bond angles (sp3 hybridization) no LP on central atom so molecular geometry is tetrahedral Examples are: CH4, XeO4, CCl4, SiH4, ClO4-, NH4+ one LP on central atom so molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal (tripod) Examples are: NH3, PF3, H3O+, XeO3, ClO3 two LPs on central atom so molecular geometry is bent Examples are: H2O, OF2, H2S, SF2 5 domains - domain geometry trigonal bipyramidal, 90°/120° bond angles (sp3d hybridization) no LP on central atom so molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal Examples are: PCl5, SOF4, AsF5 one LP on central atom so molecular geometry is see-saw Examples are: SF4, IF4+, IO2F2-, XeO2F2 two LPs on central atom so molecular geometry is T-shaped Examples are: ClF3, BrF3 three LPs on central atom so molecular geometry is linear Examples are: XeF2, I3-, IF2- 6 domains - domain geometry octahedral, 90° bond angles (sp3d2 hybridization) no LP on central atom so molecular geometry is octahedral Examples are: SF6, IOF5 one LP on central atom so molecular geometry is square pyramidal Examples are: IF5, TeF5-, XeOF4 two LPs on central atom so molecular geometry is square planar Examples are: XeF4, ICl4- Here are the same forty-six molecules and ions in random order. Write the Lewis structure and determine the domain geometry for each. Then predict the molecular geometry and find it in the above table to check. NO3-, TeF5-, SF4, CO32-, H2S, PCl5, BF3, NH4+, AsF5, HCN, XeO2F2, ClO4-, XeF4, I3-, H3O+, ClF3, SO2, O3, NO2-, XeOF4, PF3, SF6, CH4, XeF2, XeO4, SO3, CCl4, SiH4, PbCl2, NH3, XeO3, ClO3-, H2O, OF2, SF2, CO2, SOF4, IF4+, IO2F2-, BeCl2, BrF3, IF2-, IOF5, IF5, C2H2, ICl4- http://alpha.fdu.edu/~strange/LINKS/shapes04.html