Chapter 17 - Palmer ISD
advertisement

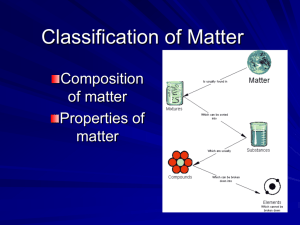
Chapter 17 Section 1—Composition of Matter Section 1 • Pure Substances– Either an element or a compound that cannot be broken down into simpler components and still maintain the properties of the original substance ex: helium, aluminum, water, salt Elementsa substance whose atoms are all alike *there are 90 found in nature/20 others made in labs • Compounds – A substance in which the atoms of two or more elements are combined in a fixed proportion • Ex: water, chalk, etc. • Compounds usually look different from the elements in them (salt—Na and Cl) • Mixtures– A material made up of two or more substances that can be easily separated by physical means – Heterogeneous Mixtures: • A mixture in which different materials can be distinguished easily • Ex: granite, concrete, pizza • Homogeneous Mixtures: • Contains two or more gaseous, liquid or solid substances blended evenly throughout • Ex: soft drinks, vinegar, etc • Solution• A homogeneous mixture of particles so small that they cannot be seen with a microscope and will never settle to the bottom of their container – Ex: – Colloid: – A type of mixture that never settles – It’s particles are larger than those in solutions but not heavy enough to settle – Ex: some paints, shampoos, hairgel, • Tyndall Effect: • The scattering of light by colloidal particles • A light beam is invisible as it passes through a solution, but can be seen readily as it passes through a colloid – Ex: pg. 523 • Suspensions: • A heterogeneous mixture containing a liquid in which visible particles settle – ex: muddy pond water (visible particles settle out eventually) SECTION 2—Properties of Matter • Physical Properties• Any characteristic of a material that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance – Ex: color, shape, size, melting/boiling pt, etc. Physical Properties may be used to separate substances (in a mixture) • Physical change a change in size, shape or state of matter (might involve energy changes but element or compound itself does not change) *PHYSICAL CHANGES ARE PHASE CHANGES!! Distillationprocess for separating substances in a mixture by evaporating a liquid and recondensing its vapor • Chemical properties – A characteristic of a substance that indicates whether it can undergo a certain chemical change – Ex: flammability, exposure to light Chemical Change: A change of one substance to another Ex: foaming of antacid tablets, silver tarnishing, etc. *A NEW SUBSTANCE IS FORMED BY A CHEMICAL CHANGE!!!! Weathering—Chemical or Physical? • Some weathering changes are physical and some are chemical • Physical—rocks split, streams cut through rock, etc. • Chemical—calcium carbonate from limestone changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate – Ex: White Cliffs of Dover The Conservation of Mass • Law of Conservation of Mass Matter is neither created nor destroyed (during a chemical change) The mass of all substances that are present before a chemical change EQUALS the mass of all the substances that remain after the change