PVTn Gas Law Problems Worksheet - Chemistry
advertisement
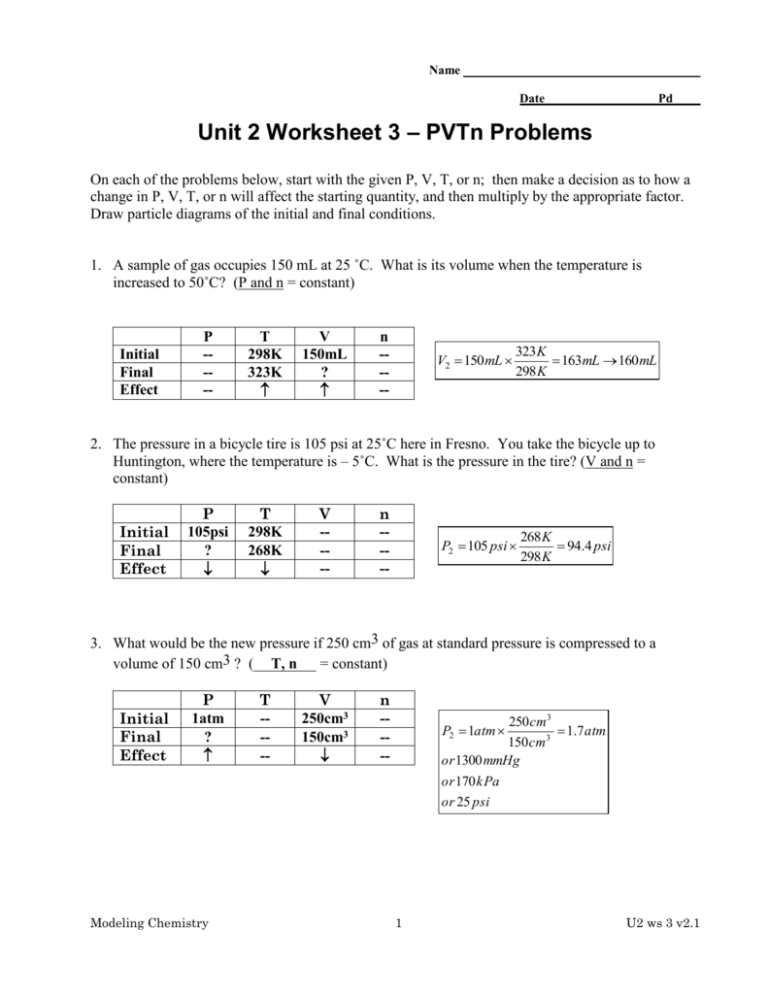
Name Date Pd Unit 2 Worksheet 3 – PVTn Problems On each of the problems below, start with the given P, V, T, or n; then make a decision as to how a change in P, V, T, or n will affect the starting quantity, and then multiply by the appropriate factor. Draw particle diagrams of the initial and final conditions. 1. A sample of gas occupies 150 mL at 25 ˚C. What is its volume when the temperature is increased to 50˚C? (P and n = constant) Initial Final Effect P ---- T 298K 323K V 150mL ? n ---- V2 150 mL 323 K 163mL 160 mL 298 K 2. The pressure in a bicycle tire is 105 psi at 25˚C here in Fresno. You take the bicycle up to Huntington, where the temperature is – 5˚C. What is the pressure in the tire? (V and n = constant) Initial Final Effect P 105psi ? T 298K 268K V ---- n ---- P2 105 psi 268 K 94.4 psi 298 K 3. What would be the new pressure if 250 cm3 of gas at standard pressure is compressed to a volume of 150 cm3 ? ( T, n = constant) Initial Final Effect P 1atm ? Modeling Chemistry T ---- V 250cm3 150cm3 n ---- 250 cm3 1.7 atm 150 cm3 or 1300 mmHg or 170 kPa or 25 psi P2 1atm 1 U2 ws 3 v2.1 4. What would be the new volume if 250 cm3 of gas at 25˚C and 730 mm pressure were changed to standard conditions of temperature and pressure? (__n__= constant) P Initial Final Effect 730mmHg 760mmHg T 298K 273K V 250cm3 ? P T n ---- V2 250cm3 730 mmHg 273 K 220cm3 760 mmHg 298 K 5. Sam’s bike tire contains 15 units of air particles and has a volume of 160mL. Under these conditions the pressure reads 13 psi. The tire develops a leak. Now it contains 10 units of air and has contracted to a volume of 150mL). What would the tire pressure be now? Initial Final Effect P 13psi ? V n T ---- V 160mL 150mL n 15u 10u P2 13 psi 160 mL 10u 9.2 psi 150 mL 15u 6. A closed flask of air (0.250L) contains 5.0 “bobs” of particles. The pressure probe on the flask reads 93 kPa. A student uses a syringe to add an additional 3.0 “bobs” of air through the stopper. Find the new pressure inside the flask. Initial Final Effect P 93kPa ? T ---- V ---- n 5bobs 8bobs P2 93kPa 8bobs 150 kPa 5bobs 7. A 350 mL sample of gas has a temperature of 30˚C and a pressure of 1.20 atm. What temperature would needed for the same amount of gas to fit into a 250 mL flask at standard pressure? Initial Final Effect P 1.2atm 1atm Modeling Chemistry T 303K ? P V V 350mL 250mL n ---- T2 303 K 2 1atm 250 mL 180 K 1.2atm 350 mL U2 ws 3 v2.1 8. A 475 cm3 sample of gas at standard temperature and pressure is allowed to expand until it occupies a volume of 600. cm3. What temperature would be needed to return the gas to standard pressure? Initial Final Effect P ---- T 273K ? V 475cm3 600cm3 n ---- T2 273 K 600cm3 345 K 475cm3 9. The diagram below left shows a box containing gas molecules at 25˚C and 1 atm pressure. The piston is free to move. In the box at right, sketch the arrangement of molecules and the position of the piston at standard temperature and pressure. Does the volume decrease significantly? Why or why not? 273 K 298 K V2 0.92 V1 V2 V1 Modeling Chemistry The volume will decrease by about 10%. 3 U2 ws 3 v2.1