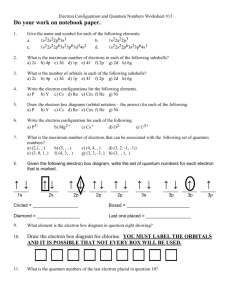
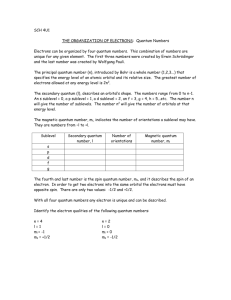
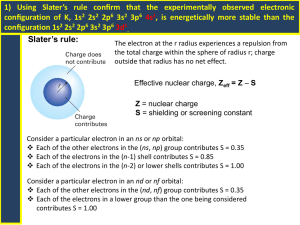
TEST 5 Answers CHEM 11 Atomic Structure NAME:
advertisement

Practice TEST 5 Review Answers CHEM 11 Atomic Structure (The actual test has 50 fill in the blanks with a word bank and 50 multiple choice questions.) 1. The substance that is the dissolving medium, usually water, is called the: (a) solute, (b) solvent, (c) Ion. 2. The separation of ions of ionic compounds during the solution process: (A) Dissociation, (b) Ionization, (c) Dissolving, (d) solutation. 3. Most ionic compounds form: (a) good electrolytes, (b) poor electrolytes. 4. Electrolytes: (a) conduct electricity, (b) do not conduct electricity. 5. Acids and bases are molecular compounds that are: (a) good electrolytes, (b) poor electrolytes. 6. Most molecular compounds form: (a) good electrolytes, (b) poor electrolytes. 7. Dissolving solutes in water involves 3 steps: (1) The solvent particles separate, (2) The solute particles separate, and (3) The solute particles attract and bond to the solvent particles. Steps 1 and 2 are: (a) endothermic or (b) exothermic. 8. When some solutes dissolve the solution gets hot. With others the solution gets cold. In cold packs what compound is used: (a) Ammonium nitrate, (b) Aluminum nitrate, (c) Ammonium sulfate, (d) Copper tetrachloride. 9. The first person to express the view that matter is composed of minute particles which was the beginning of the first atomic theory was: (a) Democritus, (b) Empedocles, (c) Aristotle, (d) Sennert, (e) Rutherford.6. 10. Which of the following statements is NOT part of Dalton's atomic theory? (a) All matter is composed of atoms. (b) An atom contains a dense central nucleus. (c) Atoms can combine to form compounds. (d) Atoms of different elements are quite different. 11. The law of multiple proportions was first stated by: (a) Millikan, (b) Dalton, (c) Avogadro, (d) Gay-Lussac, (e) Bohr. 12. In 1897 __________ used the Cathode Ray Tube to discover the electron and determined its charge to mass ratio (a) J.J. Thompson, (b) Dalton, (c) Avogadro, (d) Gay-Lussac, (e) Bohr. 13. Thompson’s model of the atom was: (a) planetary, (b) like plum pudding, (c) Was similar to the model we have today. 14. The actual charge of an electron was discovered using an oil drop experiment by: (a) Millikan, (b) Dalton, (c) Avogadro, (d) Gay-Lussac, (e) Bohr. 15. Which one of the following discoveries was not essential to perform the gold foil experiment: (a) Polonium, (b) photographic film, (c) D.N.A. 16. The planetary model of the atom was stated by: (a) Millikan, (b) Dalton, (c) Avogadro, (d) Rutherford, (e) Bohr. 17. The first person to discover the nucleus: (a) Democritus, (b) Empedocles, (c) Aristotle, (d) Sennert, (e) Rutherford. 18. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment added to our knowledge of atomic structure. How? (a) Determined the charge on an electron, (b) Determined the charge to mass ratio of the electron, (c) Determined that the atom has a central “core” or nucleus, (d) Discovered the planetary model of the atom. 19. He proposed that orbiting electrons extend in three dimensions: (a) Millikan, (b) Schrodinger, (c) Louise de Broglie, (d) Born, (e) Bohr. 20. Which subatomic particle contributes the least to the mass of an atom? a. nucleon b. electron c. proton d. neutron 21. Energy is related to the frequency of light by ___. (a) Planck's constant (b) Thomson's charge/mass ratio (c) Avogadro's number (d) the Rutherford-Bohr model 22. Which of the following ideas of the Bohr model is not retained in the modern theory of atomic structure? a. Electrons can absorb or emit energy only in whole numbers of photons. b. Atoms have a central positively charged nucleus. c. Electrons move around the nucleus as planets orbit the sun. d. Most of the volume of an atom is empty space. 23. A quantum of radiant energy is a(n): (a) ion, (b) isotope, (c) photon, (d) element, (e) nucleon. 24. Quantum theory was discovered by: (a) Millikan, (b) Planck, (c) Avogadro, (d) Rutherford, (e) Bohr. 25. The emission of electrons from the surface of a metal when struck by light is the: (a) photoelectric effect, (b) electromagnetic radiation, (c) spectrum. 26. The idea that it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of an object at the same time is the uncertainty principle proposed by: (a) Millikan, (b) Schrodinger, (c) Louise de Broglie,(d) Heisenberg, (e) Bohr. 27. The idea that no two electrons can have exactly the same set of quantum numbers is set forth in the: (a) Heisenberg’s probability position, (b) Pauli exclusion principle, (c) Plank’s constant, (d) the diagonal rule. 28. The concept that energy is given off in discrete packets rather than continuously is expressed in the: (a) photon theory, (b) quantum theory,(c) electromagnetic theory, (d) photoelectric effect. 29. Equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of pressure and temperature contain the same number of molecules is a law originally stated by: (a) Millikan, (b) Dalton, (c) Avogadro, (d) Gay-Lussac, (e) Bohr. 30. The rule that electrons will enter empty orbitals of a sublevel before they pair up (show a maximum number of unpaired electrons in a sublevel!) is: (a) Millikan’s rule, (b) Hund’s rule, (c) Gay-Lussac’s rule. 31. The mass and charge of a proton are respectively ___. (a) 1 and -1 (b) 1 and +1 (c) 0 and +1 (d) 0 and –1 32. The difference in mass of isotopes of the same element is due to different numbers of ________ in the nucleus. (a) protons (b) neutrons (c) electrons (d) positrons 33. Most atoms have a diameter between ___ nanometers. a. 0.1 and 0.5 c. 10 and 100 b. 1 and 10 d. 10 000 and 1 000 000 34. In the free, or uncombined, state the number of protons in the nucleus of an element must equal the ___. (a) mass number (b) number of neutrons in the nucleus (c) mass number - the atomic number (d) number of electrons present 35. Cu has two valence states, a +1 charge and a +2 charge. What would be the two possible Electron configurations for copper: (a) Cu = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 (b) Cu = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d6 (c) Cu = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 (d) Cu = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s3 3d8 36. Elements with full or half filled sublevels are states of special stability. This explains the decrease in ionization energy from: (a) Mg to Ar, (b) Mg to Al, (c) Na to Ar, (d) Ar to Na. 37. The maximum number of electrons that can be in the third energy level is: (a) 2, (b) 6, (c) 8, (d) 18, (e) 32. 38. The maximum number of electrons that can be in the fifth energy level is: (a) 6, (b) 8, (c) 18, (d) 32, (e) 50. 39. How many sublevels are possible in the 4th energy level: (a) 2, (b) 3, (c) 4, (d) 6, (e) 8. 40. Which quantum number describes the orientation or the space occupied by one pair of electrons in its orbital. (a) n, the principle quantum number. (b) l, the second quantum number. (c) m, the third quantum number. (d) s, the fourth quantum number. 41. Which quantum number describes the sublevels or shapes within the energy level: (a) n, the principle quantum number. (b) l, the second quantum number. (c) m, the third quantum number. (d) s, the fourth quantum number. 42. Which quantum number signifies the size of the electron cloud: (a) n, the principle quantum number. (b) l, the second quantum number. (c) m, the third quantum number. (d) s, the fourth quantum number. 43. Which quantum number describes the spin of each electron: (a) n, the principle quantum number. (b) l, the second quantum number. (c) m, the third quantum number. (d) s, the fourth quantum number. 44. The s, p, d, and f sublevels describe the probable shapes of the electron clouds. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be found in the p sublevel: (a) 3, (b) 6, (c) 9, (d) 10, (e) 18. 45. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be found in the d sublevel: (a) 3, (b) 5, (c) 7, (d) 9, (e) 18. 46. How many electrons can be in one orbital: (a) 1, (b) 2, (c) 4, (d) 8. 47. What is the largest principle quantum number in the element Ca? (a) 3, (b) 4, (c) 5, (d) 7, (e) 9. 48. Which one of the following charge clouds are spherical in shape? (a) s, (b) p, (c) d, or (d) f. 49. Which one of the following charge clouds are dumbbell in shape? (a) s, (b) p, (c) d, or (d) f. 50. Each electron in an atom can be identified by a unique set of four: (a) Orbitals, (b) quantum numbers, (c) spectrum numbers, (d) dimensions. 51. The energy levels of an atom are each designated by the: (a) second quantum number, (b) principle quantum number, (c) third quantum number. 52. The letters s, p. d, or f are used to designate a particular______ within an energy level. (a) sublevel, (b) space, (c) spin, (d) color. 53. The space that may be occupied by a pair of electrons within a sublevel is a(n): (a) orbital, (b) Plank’s space, (c) Heisenberg’s probability position. 54. A system for predicting the order of filling energy sublevels with electrons is the: (a) Heisenberg’s probability position, (b) Plank’s constant (c) Pauli exclusion principal, (d) the diagonal rule. 55. Which is the largest of the first 26 elements? (a) Li, (b) Ar, (c) F, (d) Fe, (e) K. 56. As the principal quantum number increases from top to bottom in a group the size of the charge cloud: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 57. As the atomic number increases from left to right across a period the size of the charge cloud: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 58. The radii of the atoms become smaller from sodium to chlorine across period three. This is primarily due to: a) the shielding effect b) the increased number of electrons c) increased nuclear charge d) decreased metallic character. 59. The largest elements in a period are: (a) metalloids (b) metals (c) non-metals (d) size is not affected. 60. When a metallic atom from group 2 ionizes, its size: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 61. When a non-metallic atom from group 6 or 7 ionizes, its size: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 62. Electron affinity: (a) energy needed to lose one electron from a compound, (b) energy needed to lose one electron, (c) energy needed to add an electron to a gaseous atom. 63. The metal with the highest melting point of all metals is: (a) Copper, (b) Iron, (c) Tungsten, (d) Wolframite. 64. The most reactive non-metals are the: (a) Alkali metals Transition metals (d) Halogens, (e) Nobel gases. (b) Alkali earth metals (c) 65. Ionization energy is the: (a) energy needed to gain one electron, (c) energy needed to remove an electron from the –1 ion. 66. As the principal quantum number increases from top to bottom in a group the ionization energy: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 67. As the atomic number increases from left to right across a period the ionization energy: (a) decreases, (b) increases then decreases, (c) increases, (d) remains the same. 68. Which of the following does NOT affect the ionization energy of an electron: (a) the distance of the electron from the nucleus (b) the number of neutrons present in the nucleus (c) the number of energy levels in the atom (d) the charge on the nucleus. 69. Elements with low ionization energies: (a) have low electronegativities (b) are metals, (c) have low electron affinities, (d) all of these. 70. Which of the following would correctly characterize a nonmetal? (a) low ionization energy, low electron affinity (b) high ionization energy, low electron affinity (c) high ionization energy, high electron affinity (d) low ionization energy, high electron affinity. 71. When a metallic atom ionizes: (a) it gains electrons, (b) it loses electrons, (c) it neither gains nor loses electrons. 72. Which of the following has the largest atomic radii? (a) carbon (b) silicon (c) lead (d) tin (e) selenium. 73. What property do all elements of a family have in common? (a) reactivity (b) electron affinity (c) solubility (d) ionization energy (e) outer electron configuration. 74. Compared to the stability of the original atom, the stability of its ion that resembles a noble gas configuration would be: (a) identical (b) sometimes less (c) less (d) greater 75. The ___ have the lowest electronegativities. (a) nonmetals (b) metalloids (c) metals 76. The factor(s) that influence electronegativity is/are ____ (a) nuclear charge of the atom (b) atomic radius of the atom (c) the shielding effect (d) all of the preceding. 77. If an element has 6 electrons in its outside level its predicted charge would be: (a) +3 (b) -2 (c) -3 d) none of these. 78. The ability to conduct electricity readily is a property of: (a) nonmetals (b) semiconductors (c) metals (d) halogens. 79. The predicted charge on the ion of B is ____. (a) +3 (b) +6 (c) -6 (d) +4 (e) +2 80. Which of the following are harder, denser and stronger: (a ) Alkali metal (b) Alkali earth metal_____________________________ For the following elements, what category would they be found: (a) Alkali metal (b) Alkali earth metal (c) Transition metals (d) Halogen, (e) Nobel gases . 81. Potassium, 83. Co, (a) Alkali metal (c) Transition metals 82. Sr, (b) Alkali earth metal 84. At (d) Halogen, 85. Electronegativity is a(n): (a) attraction between positive and negative ions, (b) attraction between nonpolar molecules, (c) attraction between polar molecules, (d) measure of attraction for electrons. 86. The formation of bonds between atoms depends on __. (a) the electron configurations of the atoms involved (b) the attraction the atoms have for electrons (c) both of the preceding factors (d) neither of the preceding factors. 87. The particle that results when two or more atoms form covalent bonds is a: (a) single charged atom (b) atomic ion (c) molecule 88. The strength of the bond between two atoms ___ as the difference in their electronegativities become larger. (a) decreases (b) increases (c) remains constant (d) could increase or decrease. 89.____ compounds are normally solids at STP and tend to be soluble in water. (a) hydrogen (b) metallic (c) covalent (d) Ionic. 90. Covalent bonds form when the electronegativity difference between atoms is: (a) small (b) average (c) large (d) none of these. Classify the bonds between the following pairs of atoms as principally (a) ionic (1.8-4.0), (b) polar covalent (0.6-1.7), (c) non-polar covalent (0.0-0.5), or (d) non bonding elements. 91. Al - S (b) polar covalent (0.6-1.7), 92. Se-As (c) non-polar covalent (0.0-0.5), 93. N- O (c) non-polar covalent (0.0-0.5), 94. Ba - Cl . (a) ionic (1.8-4.0), 95. K - F (a) ionic (1.8-4.0), 96. He -Ar (d) non bonding elements. 97. The London dispersion force is: (a) attraction between positive and negative ions, (b) attraction between nonpolar molecules, (c) attraction between polar molecules, (d) measure of attraction for electrons. 98. The dipole – dipole attraction is: (a) attraction between positive and negative ions, (b) attraction between nonpolar molecules, (c) attraction between polar molecules, (d) measure of attraction for electrons. 99. When two atoms combine by sharing electrons, where one has a bigger share, in order to obtain a stable octet they form a ___ bond. (a) ionic, (b) polar covalent, or (c) non-polar covalent. 100. When two atoms combine by transfer of electrons the opposite charges of the ions attract resulting in a____bond. (a) ionic, (b) polar covalent, or (c) non-polar covalent.