Ch 1 Notes to PPT filled in
advertisement

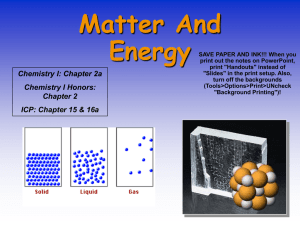
1 Sc 9 Ch 1-2 Notes: Matter Matter: Anything that has mass and volume Mass: the amount of matter in a substance Volume: The amount of space that matter occupies. Property: A characteristic used to describe matter. Qualitative – can be describe but not measured . Quantitative: can be measured . Atom: the smallest part of an element that still has the same properties of that element. Molecule: two or more atoms chemically combined. (either the same or different atoms) 2 Element: A substance that contains only one type of atom Compound: A substance that contains or more different types of atoms, Chemically combined. two Pure Substance: A substance that has the same properties in any sample you choose. Can be a element or an compound . Models :Each geometric shape represents a type of atom. When the shapes are drawn together, they represent atoms that are chemically combined. Ex. 1: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 6 # of molecules: 0 # of different types of atoms: 1 # of different types of compds 0 3 Ex. 2: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 12 # of molecules: 6 # of different types of atoms: 1 # of different types of compds0 Ex. 3: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 15 # of molecules: 5 # of different types of atoms: 2 # of different types of compds1 Ex.4 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 17 # of molecules: 7 # of different types of atoms: 3 # of different types of compds2 4 Ex.5 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 17 # of molecules: 5 # of different types of atoms: 3 # of different types of compds1 Ex.6 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: 13 # of molecules: 3 # of different types of atoms: 4 # of different types of compds0 Physical Changes: Changes in which no new substance is formed . Ex. Chemical Change: Changes in which NEW substances are formed . Ex. 5 Clues that suggest a CHEMICAL change has occurred: 1. a new colour may appear 2. gas or bubbles may be given off 3. Light or sound may be formed. 4. Solid material (a precipitate may form in a liquid 5. The change may be difficult to KMT: reverse Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. All matter is made up of particles 2. The particles are always moving 3. There is space between the particles. In a gas : space is extremely large In a liquid: medium sized space In a solid: spaces are quite small 4. To make the particles move faster you heat them up (adding energy) . 5. When the particles move faster they expand 6. When the particles expand they become less dense and will start to rise (float) . 6 7. Convection currents will be created when molecules heat up. Changes of State: State Shape Volume Solid Liquid Fixed Fixed Takes Fixed shape of container Space between molecules Small Medium (so they can just slide past one another 7 Gas Shape of Takes as V. Large container much volume as allowed