Ch 1 notes to ppt
advertisement

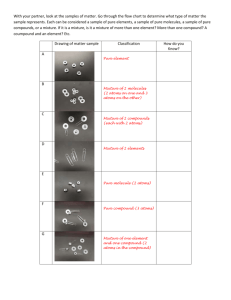
1 Sc 9 Ch 1 Notes: Matter Some Vocabulary Review to START.. Matter: Anything that has and Mass: the amount of substance Volume: The amount of matter occupies. Property: A describe matter. Qualitative – can be not . Quantitative: can be Atom: the smallest that still has the same element. in a that used to but . of an element of that Molecule: or more atoms combined. (either the or different atoms) 2 Element: A substance that contains only of Compound: A substance that contains or more types of atoms, combined. Pure Substance: A substance that has the same in any sample you choose. Can be a or an . Models :Each geometric shape represents a type of atom. When the shapes are drawn together, they represent atoms that are chemically combined. Ex. 1: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds 3 Ex. 2: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds Ex. 3: Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds Ex.4 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds 4 Ex.5 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds Ex.6 : Mixture or Pure Substance? Element Compound Both? Total # of atoms: # of molecules: # of different types of atoms: # of different types of compds Physical Changes: Changes in which new substance is . Ex. Chemical Change: Changes in which substances are . Ex. 5 Clues that suggest a CHEMICAL change has occurred: 1. a new may appear 2. or may be given off 3. or may be formed. 4. material (a may form in a liquid 5. The change may be difficult to KMT: 1. All matter is made up of 2. There is between the particles. In a gas : In a liquid: In a solid: 3. The particles are constantly . 4. To make the particles move faster you . 5. When the particles move faster they 6 6. When the particles they become less and will start to . 7. Will be created when molecules heat up. Changes of State: State Solid Liquid Gas Shape Volume Space between molecules 7 ATOMIC THEORY: DALTON THOMSON Ernest RUTHERFORD Niels BOHR 8 Today’s Model of an ATOM: