QUANTUM NUMBERS
advertisement

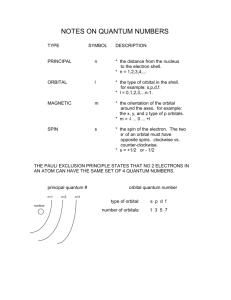
chemistry quantum numbers name: date: Quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals. Principal Quantum Number (n) - Indicates the _________________________ occupied by an electron. - Values of n must be _______________ integers. - As n increases, e- energy and average distance from nucleus increase. Ex.) An electron with n=1 has _______________ energy and is _______________ to the nucleus than an electron with n=5. - The n quantum number also sets the __________of the atom. main energy level (shell number) n=1 n=2 n=3 n=4 maximum # of orbitals in that shell (n2) maximum # of electrons in that shell (2n2) Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l) - Indicates the _______________ of the orbital. - An _______________ is defined as a region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron. - There are __________ orbital shapes that are commonly studied. - The value for the l quantum number can be _________________________. - Each value for the l quantum number corresponds to a certain orbital shape. l = 0 corresponds to a(n) ___ orbital shape l = 2 corresponds to a(n) ___ orbital shape l = 1 corresponds to a(n) ___ orbital shape l = 3 corresponds to a(n) ___ orbital shape energy level (n) n=1 n=2 n=3 n=4 # of possible orbital shapes/subshells (n) letters of subshells present in this level chemistry quantum numbers name: date: Together, the _____ and _____ quantum numbers determine the energy of a given orbital. The two numbers n and l taken together represent a _______________. The subshells are referred to by a number (__________) and a letter s, p, d, and f orbitals (__________). So, an “s” orbital can occur as 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s…etc. Likewise, “p” orbitals can occur in the 2 nd, 3rd (and so on) energy levels of the atom and would be described as 2p, 3p…etc. Some People Don’t Forget… subshells with this type of orbital s p # of orbitals in subshell total # of electrons possible d f Magnetic Quantum Number (m) Describes how many ways a given orbital can __________ space. - An “s” orbital can fill space in only __________ way. The “p” orbital can fill space in __________ ways, the “d” __________ ways and the “f” __________ ways. “s” orbital “p” orbital “d” orbital Spin Quantum Number (+1/2, -1/2) No two _______________ in the same _______________ can spin in the same direction. clockwise counter-clockwise