Practice for Midterm X

Practice for Midterm 6 – Chapter 16
Chem 1000 2004
Your responsible for the following sections of the text:
Chapter 16
Representative questions: 16.1, 3, 4,6, 9,10, 13, 17, 21, 23, 29, 35-38, 41-46, 62.
Equations
1 J = 1 kg•m 2 sec -2
E
r n
Z
2 n n
Z
2
2 a o
N o
= 6.022 x 10
23
mol -1
,
Ry Ry
2.18
x 10
18 h = 6. 626 x 10
-34
J
, a o
= 0.529Å = 5.29 x 10 -11 m
J
s c = 2. 998 x 10
8
h
, m e
= 9.11 x 10 -31 kg mv
x
( mv )
h
E = h
= hc
m
s
1 R = 8.314 J/mol•K
E = - Z
2
n
1
2
2
1 n
1
2
Ry
Question One (four marks)
A mixture of 21 moles of SO
2
and 15 moles of O
2
gas reacts to form SO
3
gas. i) If the initial total pressure is 8.4 atm, what is the partial pressure of O
2
before any reaction occurs?
Question Five
Consider an electron in a hydrogen atom that falls from the 5th shell to the 4th shell. i.) What is the wavelength of the photon emitted during this transition?
Question Six
3) In the Bohr atom, and considering only the first four “orbits” (i.e. n = 1, 2, 3 or 4), what transition will involve the emission of light of the shortest wavelength?
Question Seven
What is the frequency of yellow light with a wavelength of 562 nm?
Question One
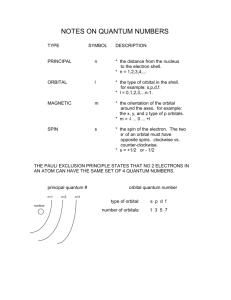
What are the three quantum nos. that are used to describe an orbital and what property is described by each quantum no.?
Question Two i) Give a set of quantum nos. that are valid for a 4f orbital. ii) How many planar nodes are present in a 4d orbital? iii) How many spherical nodes are present in a 3p orbital? iv) An orbital with m l
= -2 cannot be what kind(s) of orbitals? (spdf)
Question Three
Compare the Bohr model of the H atom with Schrödinger’s description of the H atom with respect to: i) quantum numbers ii) electron energies iii) description of electron position
Question Four
Which of the following sets of quantum nos. are invalid? Briefly explain why they are not correct.
{2, 2, 1}
{3, 1, -1}
{6, 2, 3}
Question Five i) Sketch and r 2 2 for a 2s orbital. ii) How does this orbital differ from a 1s orbital? iii) Sketch a 2p x
orbital and label the different components. iv) How does this orbital differ from a 2p y
orbital?
Question Six
Answer the following questions about the orbital below
.
i) What type of orbital is it? ii) Which quantum no. is associated with this type of orbital? iii) What is the value of this quantum no.? iv) Label the orbital diagram and indicate the following: a) all nodes b) a lobe c) phase
Question Seven i) Compare a 1s orbital and a 2s orbital of the same atom.
How are they different?
How are they the same? ii) Give a set of valid quantum nos. for a 5 d orbital.
Question Twelve (4 marks)
Which of the following sets of quantum nos. are invalid? Briefly explain why they are not correct.
{3, 3, 0}
{2, 1, 0}
{6, 5, -1}
{4, 3, -4}
Question Three (seven marks) i) Describe the Bohr model of the atom and how it offers an explanation for the origin of atomic spectra. ii) What is the radius of an electron in the fifth orbit (n=5)? iii) An electron in an H atom falls to the n = 2 orbit from a higher orbit and emits a photon with a wavelength of
410 nm. From what orbit did it fall?
Question Four (four marks)
Answer the following questions making reference to the photoelectric effect. i) When a beam of green light (530 nm) is directed on a copper surface, no electrons are ejected. What happens if the green light is replaced with red light (750 nm? Explain. ii) What happens if the intensity of the green light is increased? Explain.