Quantum Numbers Power Point
advertisement

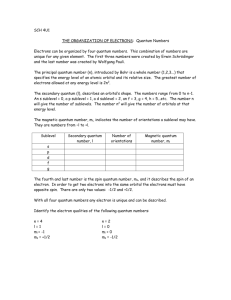
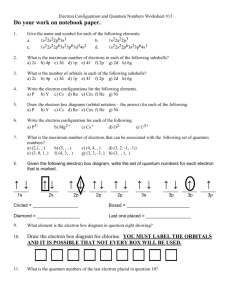
Atomic Structure Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers specify the properties of orbitals and of electrons in orbitals the first three numbers describe: main energy level (n) Shape (l) Orientation (ml) 4th describes spin of electron (ms) 1st Quantum Number (n) main energy level occupied by electron values are all positive whole # integers (1,2,3,…) As it increases, the electron: has more energy is farther from nucleus the total number of orbitals in a level is equal to n2 1st Quantum Number (n) n 1 2 3 4 # of orbitals 1 4 9 16 nd 2 Quantum Number (l) the shape of the orbital (sublevel) # possible shapes = energy level 4th energy level has 4 possible shapes possible s: 0 p: 1 d: 2 f: 3 values: 0 to n-1 2nd Quantum Number Level Sublevels Sublevels 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 0 3 3rd Quantum Number (ml) the position of an orbital around the nucleus (x, y, or z direction) has values from +l -l each orbital holds maximum of 2 electrons 4th Quantum Number (ms) the spin state of the electron only 2 possible directions only 2 possible values: +½ and -½ paired electrons must have opposite spins -1/2 +1/2 Connection to Configurations 1. 2. 3. Draw out the orbital notation for the last sublevel filled in an atom Circle the last electron inserted in that sublevel Find the four quantum numbers for that electron Example 1 What are the 4 quantum numbers for the electron of highest energy in nitrogen? Example 2 What are the 4 quantum numbers for the electron of highest energy in sulfur? Example 2 What are the 4 quantum numbers for the electron of highest energy in iron? Example 4 What are the 4 quantum numbers for the electron of highest energy in calcium?