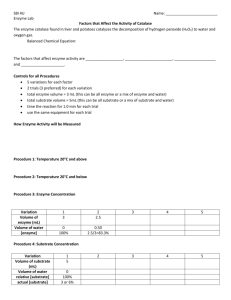
BB 450/550 Exam 1 - Oregon State University
advertisement

BB 450/550 Exam 1
Name _____________ ID #__________
Monday, October 37, 3942
General Instructions: THIS IS A PRACTICE EXAM
This exam is worth 100 points total. Read the instructions for each question
carefully. If you do not understand the instructions for a question or what is
being asked in a question, raise your hand. Be careful how you mark your exam.
If graders are uncertain about how any question is answered, it will
automatically be marked incorrect. Do not spend too much time on any one
question.
There are ***** pages in this exam, including the cover page and two pages of
numbers/equations.
Scores
Section I (33 points)
________________
Section II (32 points) ________________
Section III (35 points) ________________
Total
________________
Important items
A. The logarithm (log) of a number greater than one is a positive number.
B. The logarithm (log) of a number less than one is a negative number
C. For any number X (except X=0), log (X) = -log(1/X)
D. pH = pKa + log {[A-]/[HA]}
E. pH = -log[H+] , pKa = -Log[Ka]
F. Quadratic formula: x = (-b +/- SQRT(b2 – 4ac))/2a
G. G = G°’ + RTln[products]/[reactants]
H. R (the gas constant) = 8.3x10-3 kJ/Kmol
I. G ’ = -RTlnKeq
(Note that I would show a Table of pKa values on this exam if
needed by students for problems.)
Section I – Short answer -
The questions below can generally be answered in 15
words or less. While you will not be required to use 15 words or less, excessively
long answers will be scrutinized closely. Each correctly filled in blank below will be
awarded three points (except as noted).
1. From the syllabus, if a student wants an exam regraded, what is the time frame for
getting it in for regrading?
2. Name and describe the structure of proteins that gives rise to alpha-helices, folding,
and subunit interactions.
3. What are the primary forces stabilizing alpha helices?
4. Using a diagram, clearly illustrate the arrangement of hydrophobic and hydrophilic
amino acids in a membrane protein like porin.
5. What importance do chaperones (chaperonins) have for proteins?
6. In MALDI-TOF, what is the force that moves a particle in the instrument?
7. Why advantage does phenylisothiocyanate have for studying protein structure over
dabsyl chloride?
8. Based on what we’ve talked about in class, which of the six classes of enzymes do
serine proteases fit into?
9. For an enzyme with a high Kcat/Km, what limits the rate of its reaction?
10. What section of an enzyme does a suicide inhibitor bind? (Hint – the answer is NOT
“amino acid”)
11. In serine proteases, how is an alkoxide ion formed?
Section 2 – Calculations - For each of the problems in this section, ORGANIZE
and LABEL your calculations clearly. No partial credit will be given without
clearly labeled calculations. (each correct answer is worth 16 points)
1. You have 500 ml of an unknown buffer of concentration 0.4 M. The pH is 6.0. You
add 0.05 moles (no volume change) of NaOH to the mixture and discover there is twice
as much salt as acid in the mixture. What is the pKa of the unknown buffer?
2. A scientist discovers a compound that inhibits an enzyme by competing with the
substrate for the active site. Draw a Lineweaver-Burk plot depicting the kinetic behavior
of enzyme in the presence of this compound and the substrate compared to the substrate
alone. To be correct, your graph must CLEARLY label the graph’s axes, the uninhibited
reaction, and the inhibited reaction.
Section 3 –For each question, provide a brief explanation of the phenomenon.
Long rambling answers that are not to the point will lose points, even if they contain
part of the correct answer. Each correct answer is worth 7 points.
1. A scientist has the oligopeptide shown below
Alanine-threonine-methionine-serine-leucine-glycine-lysine-glutamic acid-aspartic acid
The oligopeptide is cleaved with trypsin and then added to a column packed with an
anion exchange resin. Give the primary structure of the first fragment to elute from the
column, if the pH is 6.
2. A scientist working with a protein in mercaptoethanol discovers that the protein is
very unstable, but when mercaptoethanol is absent, the protein is very stable. Explain the
most logical reason for these observations.
3. Describe the double displacement mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
4. Describe the relationship between the favored direction of a reaction and the presence
of an enzyme. What effect does an enzyme have on the rate of reaction and the direction
of a reaction, compared to an uncatalyzed reaction?
5. Describe what a phi/psi angle is relative to the structure of a protein.