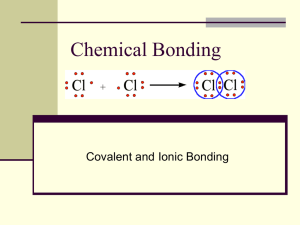
In ionic bonding, electrons are completely transferred from one atom
advertisement

In ionic bonding, electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. In the process of either losing or gaining negatively charged electrons, the reacting atoms form ions. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, which are the basis of the ionic bond. For example, during the reaction of sodium with chlorine: sodium (on the left) loses its one valence electron to chlorine (on the right), resulting in a positively charged sodium ion (left) and a negatively charged chlorine ion (right). Notice that when sodium loses its one valence electron it gets smaller in size, while chlorine grows larger when it gains an additional valence electron. This is typical of the relative sizes of ions to atoms. Positive ions tend to be smaller than their parent atoms while negative ions tend to be larger than their parent. After the reaction takes place, the charged Na+ and Cl- ions are held together by electrostatic forces, thus forming an ionic bond. Ionic compounds share many features in common: Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals. In naming simple ionic compounds, the metal is always first, the nonmetal second (e.g., sodium chloride). Ionic compounds dissolve easily in water and other polar solvents. In solution, ionic compounds easily conduct electricity. Ionic compounds tend to form crystalline solids with high melting temperatures. This last feature, the fact that ionic compounds are solids, results from the intermolecular forces (forces between molecules) in ionic solids. If we consider a solid crystal of sodium chloride, the solid is made up of many positively charged sodium ions (pictured below as small gray spheres) and an equal number of negatively charged chlorine ions (green spheres). Due to the interaction of the charged ions, the sodium and chlorine ions are arranged in an alternating fashion as demonstrated in the schematic. Each sodium ion is attracted equally to all of its neighboring chlorine ions, and likewise for the chlorine to sodium attraction. The concept of a single molecule becomes blurred in ionic crystals because the solid exists as one continuous system. Forces between molecules are comparable to the forces within the molecule, and ionic compounds tend to form crystal solids with high melting points as a result. Covalent Bonding The second major type of atomic bonding occurs when atoms share electrons. As opposed to ionic bonding in which a complete transfer of electrons occurs, covalent bonding occurs when two (or more) elements share electrons. Covalent bonding occurs because the atoms in the compound have a similar tendency for electrons (generally to gain electrons). This most commonly occurs when two nonmetals bond together. Because both of the nonmetals will want to gain electrons, the elements involved will share electrons in an effort to fill their valence shells. A good example of a covalent bond is that which occurs between two hydrogen atoms. Atoms of hydrogen (H) have one valence electron in their first electron shell. Since the capacity of this shell is two electrons, each hydrogen atom will "want" to pick up a second electron. In an effort to pick up a second electron, hydrogen atoms will react with nearby hydrogen (H) atoms to form the compound H2. Because the hydrogen compound is a combination of equally matched atoms, the atoms will share each other's single electron, forming one covalent bond. In this way, both atoms share the stability of a full valence shell. Covalent bonding between hydrogen atoms Concept simulation - Recreates covalent bonding between hydrogen atoms. (Flash required) Unlike ionic compounds, covalent molecules exist as true molecules. Because electrons are shared in covalent molecules, no full ionic charges are formed. Thus covalent molecules are not strongly attracted to one another. As a result, covalent molecules move about freely and tend to exist as liquids or gases at room temperature. Multiple Bonds: For every pair of electrons shared between two atoms, a single covalent bond is formed. Some atoms can share multiple pairs of electrons, forming multiple covalent bonds. For example, oxygen (which has six valence electrons) needs two electrons to complete its valence shell. When two oxygen atoms form the compound O2, they share two pairs of electrons, forming two covalent bonds. Lewis Dot Structures: Lewis dot structures are a shorthand to represent the valence electrons of an atom. The structures are written as the element symbol surrounded by dots that represent the valence electrons. The Lewis structures for the elements in the first two periods of the periodic table are shown below. Lewis Dot Structures Lewis structures can also be used to show bonding between atoms. The bonding electrons are placed between the atoms and can be represented by a pair of dots or a dash (each dash represents one pair of electrons, or one bond). Lewis structures for H2 and O2 are shown below. H2 H :H or H -H O2 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonding There are, in fact, two subtypes of covalent bonds. The H2 molecule is a good example of the first type of covalent bond, the nonpolar bond. Because both atoms in the H2 molecule have an equal attraction (or affinity) for electrons, the bonding electrons are equally shared by the two atoms, and a nonpolar covalent bond is formed. Whenever two atoms of the same element bond together, a nonpolar bond is formed. A polar bond is formed when electrons are unequally shared between two atoms. Polar covalent bonding occurs because one atom has a stronger affinity for electrons than the other (yet not enough to pull the electrons away completely and form an ion). In a polar covalent bond, the bonding electrons will spend a greater amount of time around the atom that has the stronger affinity for electrons. A good example of a polar covalent bond is the hydrogen-oxygen bond in the water molecule. Water molecules contain two hydrogen atoms (pictured in red) bonded to one oxygen atom (blue). Oxygen, with six valence electrons, needs two additional electrons to complete its valence shell. Each hydrogen contains one electron. Thus oxygen shares the electrons from two hydrogen atoms to complete its own valence shell, and in return shares two of its own electrons with each hydrogen, completing the H valence shells. Polar covalent bonding simulated in water The primary difference between the H-O bond in water and the H-H bond is the degree of electron sharing. The large oxygen atom has a stronger affinity for electrons than the small hydrogen atoms. Because oxygen has a stronger pull on the bonding electrons, it preoccupies their time, and this leads to unequal sharing and the formation of a polar covalent bond.