HW # 7 Solution - Lane Department of Computer Science and
advertisement

West Virginia University
Collage of Engineering and Mineral Resources
Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering
HW # 7
Solution
Signals and Systems 1, EE 327 - Fall 2002
Student Name:
ID#:
Nov. 15, 2002
Q#1
Grade:
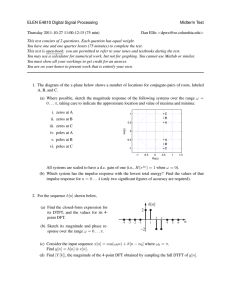
Find the transfer functions of the following discrete time systems:
a)
b)
y (k ) 0.5 y (k 1) 2 x(k ).
y (k ) 2 y (k 1) y (k 2) 2 x(k ) x(k 1) 2 x(k 2).
Solution:
a)
y (k ) 0.5 y (k 1) 2 x(k ).
Y ( z )(1 0.5 z 1 ) 2 X ( z ) H ( z )
2
2z
1 0.5 z 1 z 0.5
Solution:
b)
y (k ) 2 y (k 1) y (n 2) 2 x(n) x(n 1) 2 x(k 2).
Y ( z )(1 2 z 1 z 2 ) X ( z )( 2 z 1 2 z 2 )
2 z 1 2 z 2 2 z 2 z 2
H ( z)
2
1
2
1 2z z
z 2z 1
Q#2
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------A) Plot the poles and zeros of the following transfer functions and B) determine
the stability and C) Determine the unit step response for the following transfer
functions.
( z 0.5)
( z 2 1)
a) H ( z )
,
b) H ( z ) 2
( z 0.75)
( z 0.25)
z ( z 1)
( z 0.5)( z 0.5)
c) H ( z ) 2
,
d ) H ( z)
( z 0.5 z 0.5)
( z 2 z 0.75)
Solution:
We may rewrite them as follows:
1
a)
H ( z)
( z 0.5)
,
( z 0.75)
pole at
0.75,
zero at
0.5
( z 2 1)
( z j )( z j )
b) H ( z ) 2
( z 0.25) ( z 0.5)( z 0.5)
Poles at j , zeros at 0.5.
Plots:
z ( z 1)
z ( z 1)
( z 2 0.5 z 0.5) ( z 1)( z 0.5)
Poles at 0.5 and 1, zeros at 0 and 1.
c)
H ( z)
d)
H ( z)
( z 0.5)( z 0.5)
( z 0.5)( z 0.5)
( z 2 z 0.75)
( z 0.5 07 j )( z 0.5 07 j )
Poles at 0.86126o ,
zeros at 0.5.
Plots:
C) For step response use MATLAB. It gives the plot of step response.
>>step([1, -0.5],[1, 0.75]) % for part (a).
>>step([1, 0, 1],[1, 0, -0.25]) % for part (b).
>>step([1, -1, 0],[1, -0.5, -0.5]) % for part (c).
>>step([1, -0.25],[1, 1, 0.75]) % for part (d).
2
Q#3
Perform the graphical convolution for x[n]*h[n] where:
x[n] u[n] u[n 4], and
h[n] 0.5n u[n]
Solution:
1-Find the z transform of the following signals:
Q#4
x[n] u[n] u[n 4], and
h[n] 0.5n u[n]
Solution:
a)
x[n] u[n] u[n 4],
3
X ( z ) z n 1 z 1 z 2 z 3
n0
and
b) h[n] 0.5n u[n]
X ( z ) 0 .5 z
n
n
n0
use
(0.5 z 1 ) n
n0
geometric series
an
n0
1
1 a
if
convergence :
a 1 X ( z)
1
1 0.5 z 1
3
2- Find inverse Z transform of Y(z)=X(z).H(z) of part 1 (i. e. y(n)=inv{Y[z]}
and plot y(n). (hint: your plot should be same as plot of convolution in Q#3)
Solution:
Y(z)=X(z).H(z) is as same as y(k)=x(k)*h(k), therefore one way is using
formula of convolution as follows:
x[n] * h[n]
k
x[n]h[n k ]
k
k
(u[k ] u[k 4])0.5
nk
u[n k ]
k
n
if
0 n 4 0.5
k 0
4
if
n 4 0.5
k 0
nk
nk
1 2n 1
0.5
(0.5n 2)
1 2
n
1 25
0.5
0.5n 0.5n 5
1 2
n
Therefore for k=0, 1, 2, 3, … we get 1, 1.5, 1.75, … the same plot as problem
in Q#3. The other way is inverse (i. e. y(n)=inv{Y[z]}.
3- Find inverse Z-transform of the following signals:
( z 1)( z 0.8)
a) H ( z )
,
( z 0.5)( z 0.2)
( z 2 1)( z 0.8)
b) H ( z )
( z 0.5) 2 ( z 0.2)
Solution:
( z 1)( z 0.8)
,
( z 0.5)( z 0.2)
C3
X ( z ) C1
C2
z
z z 0.5 z 0.2
X ( z)
X ( z)
C1
z z 0 8,
C2
( z 0.5) z 0.5 1.857,
z
z
X ( z)
C3
( z 0.2) z 0.2 5.143,
z
1.857 z 5.143z
X ( z) 8
z 0.5 z 0.2
x[n] 8 [n] 1.857(0.5) n u[n] 5.143(0.2) n u[n]
a)
H ( z)
4
( z 2 1)( z 0.8)
b) H ( z )
( z 0.5) 2 ( z 0.2)
C3
X ( z ) C1
C2
C4
z
z z 0.2 z 0.5 ( z 0.5) 2
X ( z)
X ( z)
C1
z z 0 16,
C2
( z 0.2) z 0.2 5.88,
z
z
X ( z)
C4
( z 0.5) z 0.5 2.79,
z
d ( z 2 1)( z 0.8)
C3
11.12
dz z ( z 0.2) z 0.5
X ( z ) 16
5.88 z 11.12 z
2.79 z
z 0.2 z 0.5 ( z 0.5) 2
x[n] 16 [n] 5.88(0.2) n u[n] 11.12(0.5) n u[n] 2.79n(0.5) n u[n].
4- Solve the following difference equation using classical method and Ztransform method. y[k]+3y[k-1]+2y[k-2]=2x[k]-x[k-1]
where:
y[-1]=0;, y[-2]=1 and x[k]=u[k]
Solution:
See HW # 8 Solution later.
Test # 3 November 18 from chapters 6, 7 and 8.
5